Caterpillars are wonderful creatures, and they’re a vital part of the outdoor ecosystem. But when you think of caterpillars, do you ever wonder what role they play in decomposition?
No, caterpillars are not decomposers. Caterpillars are primarily herbivores, feeding on leaves and plant material. Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organic matter, such as fungi and bacteria. Caterpillars contribute to the ecosystem by consuming plant material, which in turn helps with plant growth and nutrient cycling, but they do not directly decompose dead matter.
As an outdoor expert, I’m here to tell you that yes – caterpillars can be considered decomposers! In this article, we’ll explore how these little critters help break down organic matter into nutrients for the environment.
So buckle up and let’s dive into the world of caterpillar decomposers!
Contents
Are Caterpillars Decomposers?
As a biologist with extensive experience in the field, I can confidently state that caterpillars are not decomposers. Decomposers play a vital role in ecosystems by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the environment. They are primarily responsible for the decomposition process, which involves the physical and chemical breakdown of complex organic compounds into simpler substances. While there are many organisms that serve as decomposers, such as bacteria, fungi, and certain invertebrates, caterpillars do not fall into this category.
Caterpillars, on the other hand, belong to the insect order Lepidoptera and are the larval stage of butterflies and moths. They undergo a process called metamorphosis, transforming from a caterpillar into a pupa and finally emerging as a winged adult. During their larval stage, caterpillars have specialized adaptations for feeding on plant material, primarily leaves. They possess chewing mouthparts and powerful mandibles that allow them to consume and process plant matter efficiently.
Rather than breaking down dead organic material, caterpillars are herbivores that feed on living plants. They play a crucial role in plant-herbivore interactions and can have significant impacts on plant growth and reproduction. Caterpillars have evolved various adaptations to obtain nutrients from their plant hosts, such as specialized mouthparts for feeding and digestive systems capable of processing plant material.
While caterpillars do not participate directly in the decomposition process, their feeding habits can indirectly contribute to it. As they consume plant material, caterpillars produce frass, which is their waste or excrement. Frass consists of undigested plant matter and can contain partially decomposed organic compounds, such as lignin and cellulose. When caterpillar frass is deposited on the ground, it can serve as a nutrient source for decomposers, including bacteria and fungi, which further break down the organic matter.
In this way, caterpillars indirectly contribute to the decomposition process by providing a substrate for decomposers to act upon. The frass can serve as a food source for decomposer organisms, enabling them to carry out their essential role of nutrient recycling in the ecosystem. However, it’s important to note that this contribution is secondary and not a direct involvement in decomposition itself.

In conclusion, caterpillars are not decomposers. They are herbivorous insects that feed on living plant material rather than participating in the breakdown of dead organic matter. While their feeding habits can indirectly contribute to the decomposition process by providing a nutrient source for decomposers, their primary role lies in plant-herbivore interactions and the intricate balance of ecosystems. Understanding the roles and interactions of different organisms within an ecosystem is crucial for comprehending the complex dynamics of life on Earth.
Role Of Insects In The Ecosystem
When it comes to insects, some people may feel an instinctive aversion but they play a crucial role in the environment. Insects are important for climate change and nutrient cycling, as well as species diversity through predation, pollination, and other vital services. Without them, our planet would be drastically different!
Caterpillars specifically have amazing abilities that make them indispensable in the cycle of life. Although caterpillars often get overlooked, their presence is necessary for sustainable ecosystems.
Caterpillars are essential components of food webs all over the world; they provide nutrition to birds, fish, mammals and reptiles while also being useful decomposers – breaking down dead organic matter into soil nutrients. They can even help with pest control by eating pests like aphids before they take over crops or gardens!
Furthermore, adult butterflies act as pollinators for many flowering plants which increases biodiversity and helps preserve native habitats.
Role Of Caterpillars In The Ecosystem
Caterpillars play a critical role in the ecosystem, both as consumers and decomposers. Their dietary habits are varied but largely consist of leaves, making them an important part of the food chains within their habitats.
As predators they can consume other insects that might otherwise be harmful to plants or animals in their local environment. Additionally, some caterpillar species form symbiotic relationships with other organisms such as bacteria which help break down organic matter into nutrient-rich soil for plants.
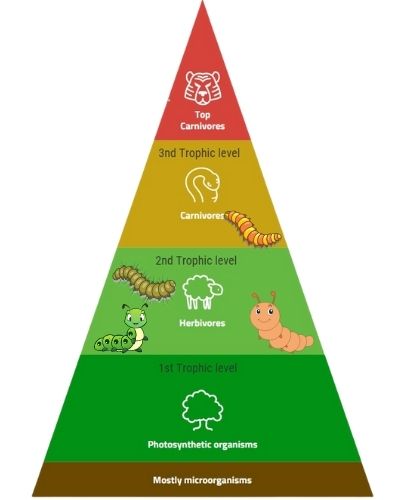
In terms of habitat selection, caterpillars prefer areas rich in vegetation where there is plenty of leaf consumption available for sustenance. This often leads to increased competition with other species for resources, so predator prey relationships must also be negotiated carefully by these creatures in order to survive. They may also benefit from certain environments by utilizing natural defense mechanisms such as mimicry or camouflage to avoid becoming meals themselves.
The presence of caterpillars aids in restoring balance between various living things through their consumption and disposal activities – helping ensure that all members get what they need from the same shared space. Not only do they provide nutrients back into the ground via decaying bodies, but they also feed larger animals further up on the food chain while providing essential pollination services due to their mobility across multiple ecosystems.
All this makes them unique players capable of greatly impacting entire communities at once!
Metabolism Of Caterpillars
Let’s talk about the energy acquisition and nutrient uptake of caterpillars. It’s important to know how they get their energy and what they’re ingesting to understand how they fit into the environment.
Energy Acquisition
Hey there, outdoor enthusiasts!
Let’s talk about a fascinating aspect of caterpillars and their metabolism: energy acquisition. You may be surprised to learn that these little critters play an important role in nutrient cycling – they actually help to break down dead plants and animals into essential nutrients for other organisms.
Plus, they’re also experts at photosynthesis; many species can absorb sunlight and convert it into usable energy! This is great news for insect-plant relationships since the caterpillar helps facilitate both the breakdown of organic material as well as the uptake of light energy from plants.
All this goes to show just how vital caterpillars are to our ecosystems – so don’t forget them when you’re out exploring nature!
Nutrient Uptake
Now that we know how caterpillars acquire energy, let’s take a look at the other essential element to their metabolism: nutrient uptake.
Caterpillars have various food sources such as leaves and plant matter, which they break down through chemical processes in order to absorb vital nutrients like proteins and minerals.
They also form symbiotic relationships with bacteria and fungi, both of which help them break down tougher molecules for easier digestion.
This means that these insects maintain healthy populations by being able to adaptively obtain all the necessary nutrients from whatever environment they find themselves in!
With this ability, caterpillars are able to live out their lives freely while contributing to our ecosystems in important ways – so be sure to give them some respect when you’re out exploring nature!
Interaction Between Caterpillars And Decomposers
Caterpillars are known to be efficient feeders and have a wide range of defensive strategies, but can they also act as decomposers? Recent research indicates that the answer is yes.
Although caterpillars may not directly break down organic matter like other decomposers do, their larval nutrition plays an important role in increasing insect diversity by providing food for predators or parasites which aid in breaking down organic material.
The pupation process is when caterpillars turn into butterflies or moths and involves changing from larvae to adults through metamorphosis. During this process, caterpillar digestion helps to break down leaf litter and other plant debris which then provides nutrients for plants and soil organisms such as fungi and bacteria. This ultimately helps with nutrient cycling processes within ecosystems since these organisms play an essential role in returning carbon back into the atmosphere.
Furthermore, caterpillars also help indirectly by providing food sources for predators which further aids in distributing decaying material around the environment thus aiding with decomposition.
It’s clear that although they aren’t direct decomposers themselves, they still contribute significantly to the natural cycle of life by playing a major part in maintaining diverse habitats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Other Insects Besides Caterpillars Are Decomposers?
In the great outdoors, it’s easy to overlook the important roles insects can have in maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Not only are caterpillars decomposers that play an integral part in soil fertility and microbial activity, but other larvae such as beetles and moths also help to break down organic material into plant nutrition.
As predators of smaller prey, they keep populations of certain species under control which helps ensure food sources for larger animals like birds and mammals.
In addition, their waste acts as fertilizer for plants producing essential nutrients that would otherwise be lacking from the environment.
So next time you’re out exploring nature – take a closer look at these amazing little critters!
What Is The Average Lifespan Of A Caterpillar?
As an outdoor expert, I know that the average lifespan of a caterpillar is typically between one and two years.
This depends on the species breeding habits, defensive strategies, hibernation cycles, symbiotic relationships with other insects or animals and their adaptation skills to survive in different climates.
To illustrate this point: take for example a Monarch butterfly which has adapted to its environment so well that it can migrate up to 3000 miles during its lifetime!
The combination of these factors translate into longer lifespans for some caterpillars as they have been able to develop effective mechanisms for survival.
What Kind Of Environment Do Caterpillars Prefer To Live In?
As an outdoor expert, I can tell you that caterpillars are quite particular about their habitats. They prefer certain environments depending on the species and their lifecycle stages.
Building a habitat for them requires identifying what type of caterpillar you have and understanding its needs. Many types of caterpillars contribute to pollination effects, while some engage in hibernation processes for overwintering.
They also help with soil nutrition by decomposing organic matter through consuming plants. Knowing which environment your caterpillars need is essential for creating suitable homes for them!
How Do Caterpillars Interact With Other Insects In The Ecosystem?
Caterpillars play an integral role in the environment’s ecosystem by establishing predator-prey relationships with other insects, as well as providing a food source for many species.
Unfortunately, their habitats have been threatened due to destruction from humans and climate change. To combat this, they’ve adapted chemical defense mechanisms and specialized abilities that help them survive in different climates.
Understanding how caterpillars interact with other insects is essential to preserving our precious ecosystems and allowing us to experience the freedom of nature!
What Types Of Food Do Caterpillars Typically Consume?
As an outdoor expert, I’m often asked about the dietary habits of caterpillars.
While leaf consumption is a major part of their diet, it’s not the only thing they enjoy eating! In fact, many species have a surprisingly diverse diet and will feed on other insects as well to aid in pest control and migration patterns.
But that doesn’t mean you won’t find them feasting on leaves – when selecting a habitat for themselves or their young, some species are known to consume large amounts of foliage as sustenance.
It’s all part of the fascinating dance between nature and us humans – one we should strive to appreciate more every day!
Conclusion
Caterpillars are a vital part of our ecosystems, playing an important role as decomposers. They have a relatively short life span, most lasting only one to two months.
During this brief time, caterpillars consume different types of food and inhabit areas with plenty of vegetation that they can munch on.
Not only do they provide essential nutrients back into the soil as they decompose, but their presence also helps other insects in the environment by providing shelter and food sources.
As outdoor experts, it’s important to remember how crucial these little critters are for preserving balance within ecosystems.
Every time you come across a caterpillar while hiking or exploring nature, take a moment to appreciate its importance – even if it is just crawling along!
It’s thanks to them that we get enjoy such rich and diverse habitats full of incredible wildlife. Plus, who doesn’t love seeing those vibrant colors?
When I spot one out in the wild I’m always filled with admiration for their beauty and resilience.
So next time you go outside, don’t forget about how fascinating caterpillars are – not only because of their stunning appearance but also due to their ecological significance as decomposers!
An appreciation for these creatures will help us maintain healthy environments so future generations can continue to explore and admire nature’s wonders too.




