Barnacles are filter feeders that live on the bottom of the sea. In the wild, barnacles form an important part of the food web since they eat a wide variety of food items and provide a nutritious meal to many other animals in the sea.
Barnacles are not primarily decomposers but can function as scavengers in the ocean. Whereas they mostly eat living things like algae, crustaceans and whales, they do also eat dying or dead animals. However, true decomposers are the bacteria and fungi that live in the barnacles’ digestive system and perform the final steps of digestion.
Barnacles are opportunistic feeders that will eat anything they can get. In the wild they mainly eat plankton, shrimp, worms, fish and whales.
Their diet changes between seasons, as different food types become more abundant, or as they grow bigger and can handle larger food items like other crustaceans.
Habitat and Behaviour of Barnacles
Barnacles are marine animals that attach themselves to other marine animals, such as whales, turtles, and ships, and feed off of the food that passes through their mouths.
Barnacles can be found in shallow areas of ocean, such as bays, estuaries, and inlets, to depths of 2000 meters.
There are over 1,000 species of barnacles, and they can be found in every ocean on Earth. Most barnacles live in shallow water, attached to rocks, shells, or other hard surfaces. A few species live in deep water, and some even live in the open ocean.
Barnacles are found in many different habitats, from the back of whales to the rocks in oceans and on the coast and from the shallow waters to the deep sea. They are also found on floating objects such as floating docks and rafts.
While most animals, including humans are able to move from one location to another at will, barnacles are not readily mobile.
Therefore, barnacles have evolved a peculiar way of moving from one location to another!
Unlike other aquatic creatures, which have fins, barnacles lack fins. Therefore, they rely on other animals, which move from one location to another for transportation. These small crustaceans usually attach themselves to whales or other large aquatic animals that are able to move.
In the ocean, the whales usually feed on plankton and other small creatures just like the barnacles!
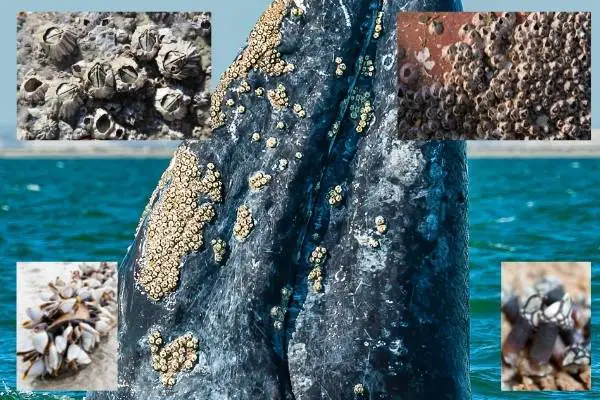

In the course of feeding, the whales move from one location to another to find food and the barnacles stick on to the whales, thus allowing them to move with them for locations with more algae and plankton to feed on!
Despite the fact that barnacles stick on to the backs of the whales and travel with them, they do not seem to cause any harm to the whales.
Primary Diet of the Barnacle
Barnacles are filter feeders, which means they feed on small plankton, detritus, and other foods floating in the water.
Some of the most common food items eaten by barnacles are:
- Algae/phytoplankton
- Cyanobacteria
- Zooplankton
- Animals they attach to
- Other detritus
Feeding Habits and Digestion of the Barnacle
Barnacles are filter feeders, using their long tentacles to capture plankton and other small organisms from the water. Some species are even able to capture small fish and crustaceans.
Most barnacles are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs. However, they usually cannot self-fertilize, and must mate with another barnacle in order to produce offspring.
Barnacles use their tube feet to attach themselves to hard surfaces. They open their mouths and filter the water around them for food. Barnacles eat by extracting particles from the water with mucus-covered plates called lophophores.
Are barnacles Carnivores, Herbivores or Omnivores?
Barnacles are omnivores because they can feed on living plants and animals as well as off of decaying matter. Most species feed off of living or dead microorganism and pieces of dead plants and animals that float by in the water.
However, some species have specialized in attaching to animals instead of rocks and ships!
The whale barnacle Coronula diadema is a carnivorous barnacle that lives only on humpback whale skin. It is a parasite of the whale’s skin and feeds on the whale’s blood, but does so without hurting the whale. In return it attracts other

Whereas they prefer feeding on living animals, they will continue to stay attached for some time after the animal dies.
Are barnacles Producers, Consumers or Decomposers?
Barnacles are consumers because they need to eat other living organisms in order to survive. Producers like plants make their own food from the sun’s energy, while decomposers break down dead matter and return it to the soil.
What Type of Consumer is a barnacle?
Whereas most species of barnacles mostly eat plant material and are therefore primary consumers, some barnacles are secondary consumers because they can consume primary consumers like herbivores. Secondary consumers sit on the trophic level above primary consumers on the food chain.
Can barnacles be Considered Decomposers?
Barnacles can eat dead or decaying matter and can therefore be considered an opportunistic detritivores or decomposers. However, this is not the main feeding strategy of barnacles, so they are mostly consumers and not decomposers.
Some barnacles, like whale barnacles, that attach to living whales will stay attached for a while after the whale is dead – effectively making them scavengers for a while!
Where are barnacles in the Food Chain?
Barnacles are considered detritivores because they feed off of decaying matter. Barnacles do not have a mouth, stomach, intestines, or digestive tract. Instead, they feed off of pieces of dead plants and animals that float by in the water.
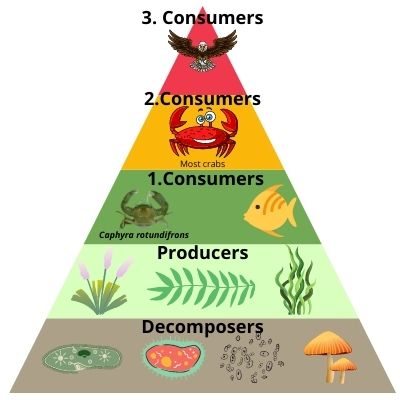
They are at the same spot in the food chain as most other crustaceans, including crabs.
Is a barnacle an Autotroph or a Heterotroph?
Barnacles are heterotrophs because they feed off of other organisms and are not able to perform photosynthesis like some bacteria, protozoa, and plants are.
What Animals Prey on barnacles?
Barnacles are prey for a wide variety of animals. They feed on decaying matter, which attracts scavengers like crabs, snails, and sea stars. They are also prey for limpets, fish, whales and even humans!
Conclusion
In this blog post, I have taken you through the diet of barnacles and how they feed on the food chain.
Barnacles are one of the most important groups of organisms in the marine ecosystem. They are filter feeders, and just like clams and mussels, they help to remove particulate matter from the water column, and they provide a source of food for a variety of animals.
Barnacles are also an important part of the food chain, as they provide a link between primary producers and higher trophic levels.
In addition, barnacles are a keystone species in many coastal habitats, and their presence or absence can have a large impact on the structure of these ecosystems.
If you are interested in the impact of other marine animals on the marine food chain, check out my other blog post on the topic!




