Beetles are a type of insect that lives in nearly every habitat on Earth. There are more than 350,000 species of beetle and they vary greatly in size, shape, and color.
Beetles tend to be herbivores (primary consumers) feeding on plants, but they may also be secondary consumers (omnivores) and also play an important role as decomposers in the ecosystem by breaking down dead and rotting plant and animal material.
They are important decomposers in forests, wetlands, grasslands, and deserts, and can be found almost anywhere on Earth.
Beetles also play an important role in the food chain as primary consumers. They eat the roots, stems, leaves, seeds, nectar, and fruits of plants. Some beetles also eat wood. The larvae (baby beetles) of some species are also parasitic and live off the blood of other animals.
While most beetles are beneficial to humans and the environment, some species can cause damage to crops or spread disease.
Contents
Primary Diet of the Beetle
Beetles are herbivores that primarily eat plant material such as roots, stems, leaves, seeds, nectar and fruits. They also eat wood that is softened by fungi. Some species of beetles are known to eat other insects and fungi as well.
The most common foods beetles eat are:
Feeding Habits and Digestion of the Beetle
Beetles use their chewing mouthparts to bite off pieces of their food. Their food is then stored in a sac-like structure called a crop where it is partially digested before being passed on to the rest of the digestive system. Beetles have a short intestine and a large hindgut where most digestion takes place.
Are Beetles Producers, Consumers or Decomposers?
Beetles are consumers. Beetles get their energy by eating either plants (producers) or primary consumers, such as other insects. Beetles, therefore, are consumers, not producers or decomposers.
Are Beetles Herbivores or Carnivores?
Beetles are primarily herbivores. They live on plant roots, stems, leaves, seeds, nectar, fruits, wood and other plant parts.
But some beetles are omnivores and these beetles are considered secondary consumers because they eat animals, typically primary consumers, such as aphids, worms or other beetles that are decomposers or herbivores.
What Type of Consumer is a Beetle?
Beetles are mostly primary consumers because they eat primarily plants, but some beetles also eat insects and are therefore secondary consumers. Generally, herbivores are primary consumers, omnivores are secondary consumers and carnivores are tertiary consumers.
Are Beetles Decomposers?
Yes, many beetles are important decomposers. Beetles that eat dead and decaying matter are decomposers.
Insects such as beetles play an important role in the decomposition process. Decomposer insects are known as detritivores, which means that they feed on decaying organic material. This process is essential for creating nutrient-rich soil, and without detritivores, the Earth would quickly become barren.
Many species of beetles play important roles in decomposition and are therefore considered detritivores. The Scarabaeidae family, for example, includes the dung beetle, which feeds primarily on feces.
The Geotrupidae family includes the earth-boring dung beetle, which bores into the ground to lay its eggs near sources of food. The Silphidae family includes the carrion beetle, which acts as a scavenger by eating dead animals.
Are all beetles decomposers?
No, the main beetle decomposers the Scarabaeidae, Geotrupidae and Silphidae families of beetles.
Are beetles decomposers in wetlands
Yes. There are many different species of beetles that are decomposers in wetlands, where the decomposition of wood is happening to a large extent. In wetlands, the primary beetles that are important decomposers are in the family of Carabidae – also known as the carpet or carpenter beetles.
Carpenter beetles
Carpenter beetles are important decomposers in wetlands and forest. Carpenter beetles are large, shiny beetles with flat, wide wings.

Carpenter beetles are important because they feed on dead wood in wetlands. They eat dead plant matter, which decomposes and creates nutrients for plants.
Carpenter beetles have chewing mouthparts, which helps them chew and digest wood. Their chewing mouthparts make holes in their host wood. Carpenter beetles also eat fungi and insects that may be found in the wood.
Are dung beetles decomposers
Yes, dung beetles are considered decomposers because they breakdown the organic material in dung into a form that can be absorbed and utilized by other animals.
Where are Beetles in the Food Chain?
Some beetles are primary consumers because they are herbivores so these are located just above decomposers in the food chain. Decomposers create the foundation of the energy pyramid and are placed at the very bottom of the food pyramid.
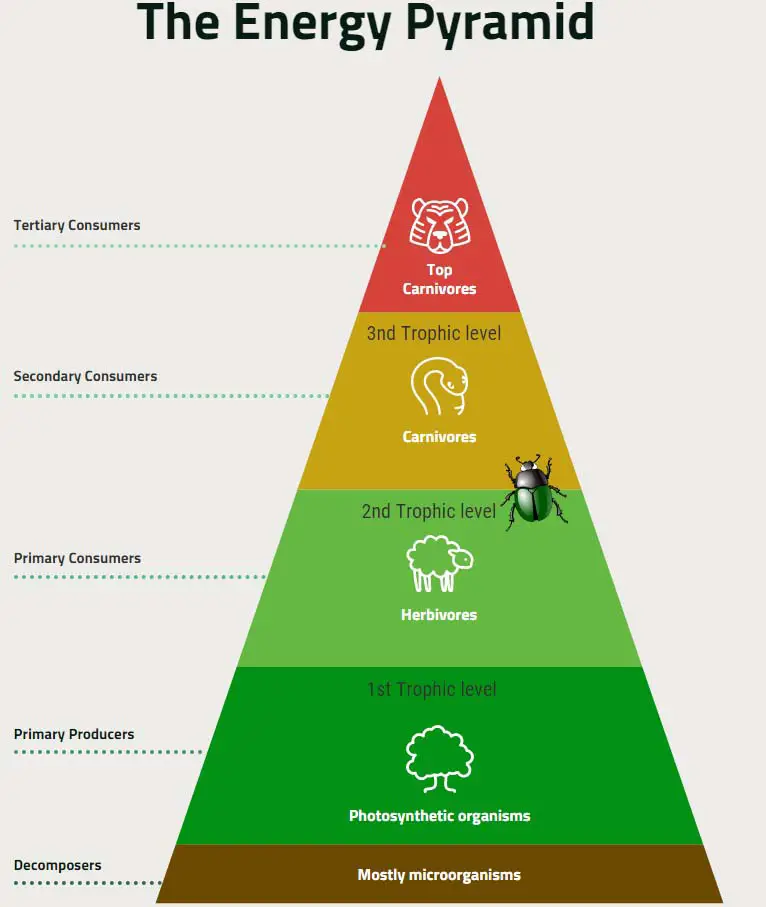
Are Beetles Autotrophs or Heterotrophs?
Beetles are heterotrophs because they eat other living organisms. Practically no animals are autotrophic because animals do not get their energy directly from the sun like plants do. That is, animals like the beetle do not make their own energy, but need to eat other organisms as their energy and carbon source.
What Animals Hunt and Eat Beetles?
Beetles are preyed upon by a variety of insects, spiders, birds, lizards (including chameleons!), amphibians, mammals, birds, fish and other animals. They are often darker colored which helps them to blend in with their surroundings to evade predators.
Conclusion
In this post I have looked into the diet of the beetle as an animal that is rarely thought about on a day to day basis.
The beetle family, or Coleoptera, contains one of the most diverse groups of organisms on the planet. There are over 350,000 species of beetles (about 25% of all known animals), and over 30,000 of these live in North America.
Beetles range in size from just a few millimeters to over several inches long. Beetles can be found on every continent except Antarctica, and can be found on all different types of land, from the tundra to the jungle. Some beetles are aquatic, but most species live on land.
Beetles are a group of insects that are commonly associated with the decomposition of organic matter, which is one of their most important functions in the ecosystems. They are often found in the soil, but they can also be found in the soil of forests, meadows and in rotting logs.
If you are interested in decomposers take a look at this article with many more examples of decomposers in the wild and why they are so important for our ecosystems!




