Wolves are carnivores that hunt in packs. They typically target large prey, such as deer or elk, but will also eat smaller animals like rabbits or rodents.
Wolves are considered to be tertiary consumers, which means they are apex predators that sit at the top of the food chain and have few natural predators.
Grey wolves are the largest member of the canine family and can weigh up to 175 pounds. They have a thick coat of fur that helps protect them from cold weather and keeps them camouflaged while hunting.
Habitat of the Wolf
Wolves live in forests, grasslands, mountains, and tundra. They can be found throughout the world. Wolves hunt in packs and are predators. They hunt large game, such as deer and elk, but also small game, such as rabbits and mice.
Primary Diet of the Wolf
Wolves hunt for large game, such as deer and elk, and small game, such as rabbits and mice. Wolves also eat carrion. Wolves are predators and scavengers. However, they will occasionally also eat berries, fruits, and plants such as dandelions and clover.
Some of the most common food items eaten by wolves are:
- Deer
- Moose
- Elk
- Caribou
- Rabbits
- Birds
- Rabbits
- Squirrels
- Fish
Feeding Habits and Digestion of the Wolf
Wolves hunt in packs. When wolves catch prey, they bite them in the neck or abdomen, killing them. Wolves usually eat their prey immediately, but they may store food to eat later. When wolves eat, they swallow food whole.
What do Baby Wolves Eat?
Baby wolves spend their first weeks of life drinking their mothers milk, after which they transition to eat meat.
Are Wolves Carnivores, Herbivores or Omnivores?
Wolves are carnivores because they primarily eat animals. Wolves do not eat plants, fruits or vegetables. They evolved from a long line of terrestrial lizards who, similarly, did not eat any plants. Even pet wolves will never eat plants. Sometimes, they may get plant matter in their gut because of the herbivore prey they ate, but this is consumed unintentionally.
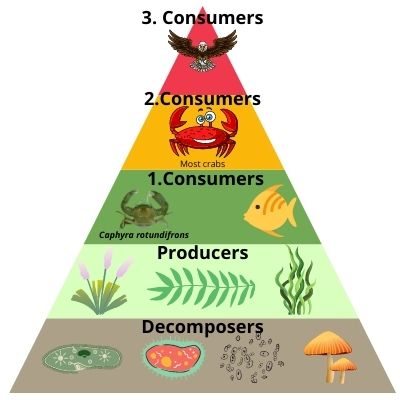
Is a Wolf a Producer, Consumer or Decomposer?
Wolves are carnivores and tertiary consumers. Wolves are consumers because they eat other living things. Only plants as well as some bacteria and protozoa are producers. Wolves are not decomposers.
What Type of Consumer is a Wolf?
Wolves are tertiary consumers because some of the animals eaten by wolves also eat animals! Generally, herbivores are primary consumers, omnivores secondary consumers and predators are tertiary consumers.
Can Wolves be Considered Decomposers or Scavengers?
Whereas wolves may occasionally eat dead animals or carrion, they are not considered decomposers, but may sometimes act as scavengers.
They do seek out dead animals and will eat their flesh if they get the chance. When eating dead animals, they can act as everything from secondary to quaternary consumers.
However, the bacteria in the guts of wolves may be considered decomposers. Therefore, no wolf species are decomposers because decomposers are mainly bacteria and fungi.
Where are Wolves in the Food Chain?
As predators, wolves sit at the top of the food chain and are considered tertiary consumers. The vast majority of a wolf’s diet is composed of small mammals like rodents and birds, but they may also eat other wolves or frogs that themselves consume animals.
The wolf is a species of concern and a symbol of nature. Wolves are often perceived as dangerous, but are actually a keystone species. Wolves are also an integral part of the ecosystem.
Wolves may not be the most common large carnivore in the US, but they are a keystone predator. This means that they are essential to the health of the ecosystem.
When the wolf population is in balance, the ecosystem benefits from the presence of wolves (see video at the end!).
Wolves help prevent the overpopulation of prey animals as well as the decline of other species of animals.
When the wolf population is in balance, the ecosystem benefits from the presence of wolves. Wolves help prevent the overpopulation of prey animals as well as the decline of other species of animals.
Are Wolves Autotrophs or Heterotrophs?
Wolves are heterotrophs because they eat other living organisms. Practically no animals are autotrophic because animals do not get their energy directly from the sun like plants do. That is, animals like the wolves do not make their own energy, but need to eat other organisms as their energy and carbon source.
What Animals Hunt and Eat Wolves?
While wolves may be at the top of the food chain, they are not without their own predators. Although adult wolves have less to fear, some animals will try to attack new born wolves for food.
Some of the most common predators of baby wolves are pumas, other wolves and even large birds like eagles. Humans also pose a threat to wolves through hunting and habitat destruction.
Conclusion
I have looked into the diet of the wolf as a carnivore, and how they mostly eat as secondary consumers but are in fact tertiary consumers.
Carnivores are a group of animals that eat meat. Carnivore animals are not restricted to eating herbivores, but may also eat other carnivores that eat meat.
Carnivores are an important part of the food chain because they eat the prey of other animals.
In the food chain, wolves are top predators, and this means that they are the ones at the end of the food chain.
If you would like more information on the food chain, please check out my other blog posts on this topic.




