The Groundhog, also known as the woodchuck, is a remarkable creature known for its ability to predict the arrival of spring. However, there are several other animals that share physical characteristics or behavior patterns similar to groundhogs.
In this article, we will explore 30 animals that resemble groundhogs in some way.
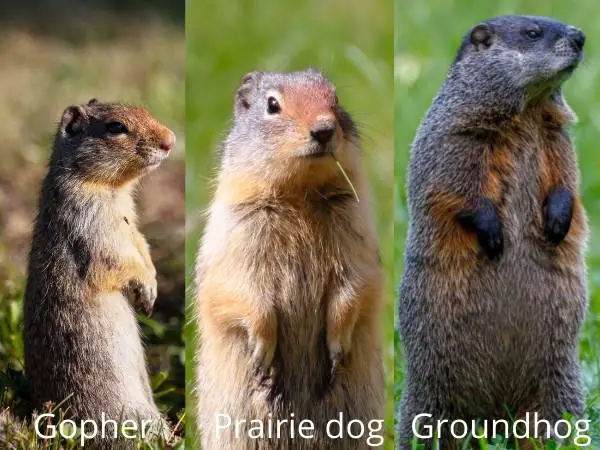

Beginning with animals that closely resemble groundhogs, we have:
Animals that closely resemble groundhogs:
- Marmots – Close relatives of groundhogs, marmots are larger rodents found mainly in mountainous areas and are known for their whistle-like alarm calls.
- Prairie Dogs – These social rodents, native to the grasslands of North America, live in extensive underground colonies and communicate with a series of complex vocalizations.
- Ground Squirrels – These squirrels live on or under the ground rather than in trees. They can be found in various habitats and are known for their burrowing behavior.
- Gophers – Small, burrowing rodents with strong forelimbs for digging. They create extensive tunnel systems and are often considered pests in gardens and farmlands.
- Susliks (European ground squirrels) – Small rodents found mainly in Europe. Their appearance and burrowing behavior make them akin to groundhogs.
Animals that share similar physical characteristics with groundhogs:
- Beavers – Large, semi-aquatic rodents known for building dams and lodges. Their flat tails and webbed feet are distinct features.
- Nutrias – Also known as river rats, nutrias are semi-aquatic rodents originally from South America but have been introduced to other parts of the world. They are often mistaken for beavers or muskrats.
- Capybaras – The world’s largest rodent, native to South America. They have a calm demeanor and are often found near bodies of water.
- Coypus – Another name for nutrias.
- Chinchillas – Native to the Andes Mountains, chinchillas have incredibly soft fur and are often bred in captivity for the pet trade or for their pelts.
- Muskrats – Semi-aquatic rodents associated with wetland habitats. They have similar body shapes and fur textures as groundhogs.
- Agoutis – Rodents native to Central and South America. While they possess a similar size and body shape as groundhogs, they have longer legs.
Animals with groundhog-like behavior patterns:
- Meerkats – Small, carnivorous mammals native to Africa. They live in groups and often stand on their hind legs to keep a lookout for predators.
- Tasmanian Devils – Carnivorous marsupials native to Tasmania. They have a fierce demeanor and are known for their strong jaws and loud vocalizations.
- Raccoons – Nocturnal mammals known for their masked faces and dexterous hands. They are highly adaptable and often found in urban environments.
- Badgers – Stout-bodied, burrowing mammals known for their digging skills. They have strong limbs and sharp claws for excavating their dens.
- Potoroos – Small marsupials from Australia that have digging habits similar to groundhogs.
- Aardvarks – Nocturnal mammals from Africa that burrow in search of ants and termites. Their digging behavior is reminiscent of groundhogs.
By understanding these animals that look like groundhogs, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity found in the animal kingdom and the fascinating adaptations that have evolved in different species. Whether it’s their physical resemblance or behavioral traits, these animals provide interesting insights into the natural world.
Contents
What Animals Look Like Groundhogs?
Curious to know which animals bear a striking resemblance to groundhogs?
- Animals that resemble groundhogs include marmots, prairie dogs, woodchucks, ground squirrels, and gophers.
- Animals that share similar physical characteristics with groundhogs include beavers, nutrias, capybaras, coypus, and chinchillas.
- Animals with groundhog-like behavior patterns include meerkats, bobcats, Tasmanian devils, raccoons, and badgers.
Get ready to dive into the intriguing world of animal look-alikes! We’ll explore a range of fascinating creatures that could easily be mistaken for our furry friends.
| Animal Name | Digging Burrows | Bushy Tails | Fur Lined Cheeks | Short Legs | Strong Claws | White Incisors | Loud Whistles |
| Marmots | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Prairie Dogs | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Groundhogs | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Ground Squirrels | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Gophers | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
From marmots to prairie dogs, woodchucks to ground squirrels, and gophers galore, each sub-section will unveil an array of astonishing similarities.
Brace yourself for a wild journey through the animal kingdom, where nature’s doppelgängers await!
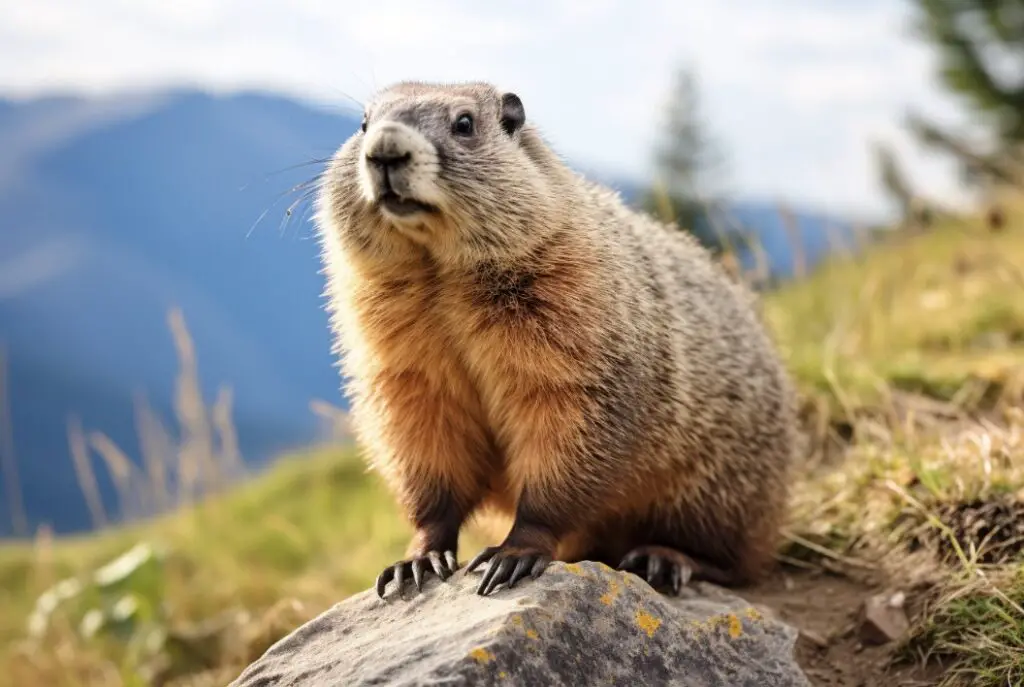
1. Marmots
To provide a clear and concise comparison of marmots to groundhogs, a table is created below.

| Characteristic | Groundhogs | Marmots |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | North America | Eurasia and North America |
| Size | 16-26 inches (40-66 cm) long | 13-28 inches (33-71 cm) long |
| Weight | 4-15 pounds (2-7 kg) | 4-14 pounds (2-6.5 kg) |
| Fur Color | Brown | Varies (brown, black, gray, or tan) |
| Digging Ability | Excellent burrowers | Excellent burrowers |
| Lifestyle | Diurnal | Diurnal |
| Diet | Herbivorous | Herbivorous |
| Hibernation | Yes | Yes |
Marmots, just like groundhogs, are excellent burrowers and inhabit similar environments. Their size and weight range are also quite similar.
While groundhogs are exclusively found in North America, marmots have a wider distribution, occurring in both Eurasia and North America.
Marmots display more variation in fur color compared to groundhogs. Both species are diurnal and primarily herbivorous, feeding on grasses, fruits, and herbs. They also hibernate during the winter months.
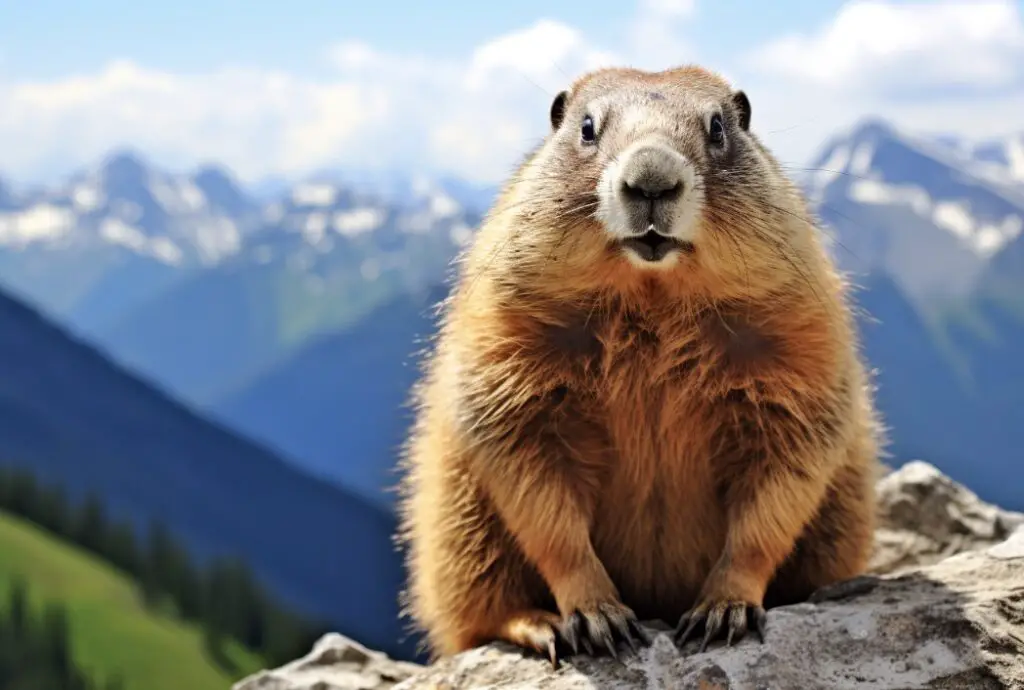

In summary, marmots share several similarities with groundhogs, including their burrowing behavior, diet, and hibernation habits. Marmots have a wider geographic range and exhibit more variation in fur coloration. Whether you’re fascinated by groundhogs or interested in learning about related species, marmots offer an intriguing comparison.
2. Prairie Dogs
When considering animals that resemble groundhogs, Prairie dogs are one of the species to look into.
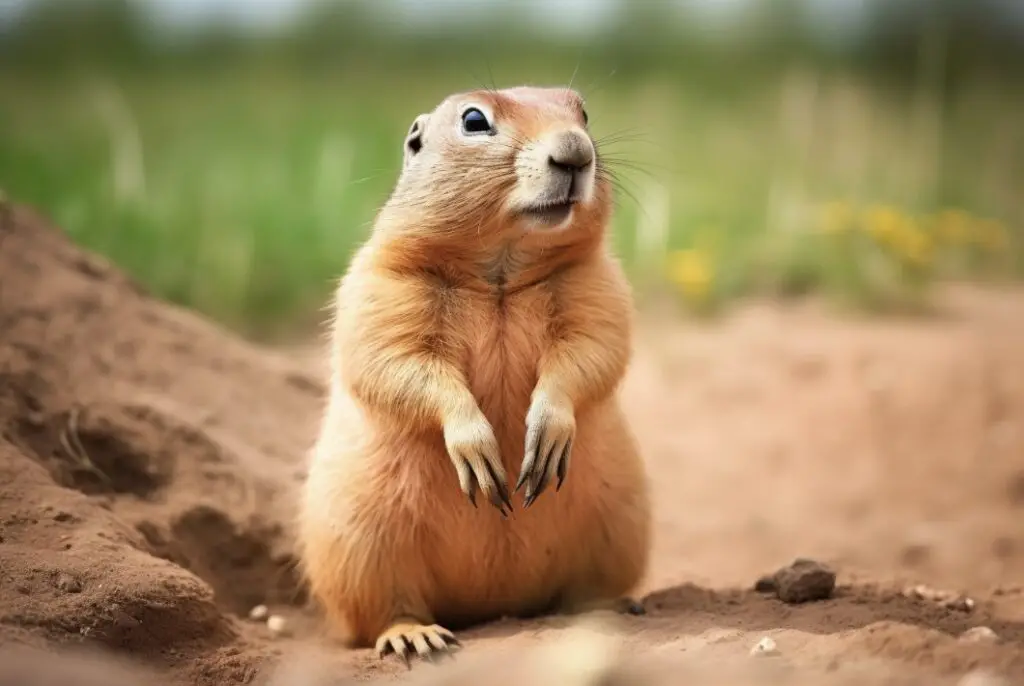

Prairie dogs, like groundhogs, belong to the rodent family, and they share similar physical characteristics and behavior patterns.
Prairie dogs are social animals that live in large colonies called towns. Within these towns, they dig complex burrow systems with different chambers for specific purposes such as nesting, sleeping, and storing food. These burrows help protect them from predators and extreme weather conditions. In terms of physical appearance,
Prairie dogs have short legs and strong claws, which allow them to effectively dig their burrows. They also have fur-lined cheeks, which they use to carry food back to their burrows. Their tails are not as bushy as groundhogs’, but they serve a similar purpose in helping with balance and communication.
Similar to groundhogs, prairie dogs have white incisors that they use for gnawing on vegetation and building their burrows. They also communicate with each other using loud whistles to alert the colony of possible danger. If you’re looking for animals that resemble groundhogs,
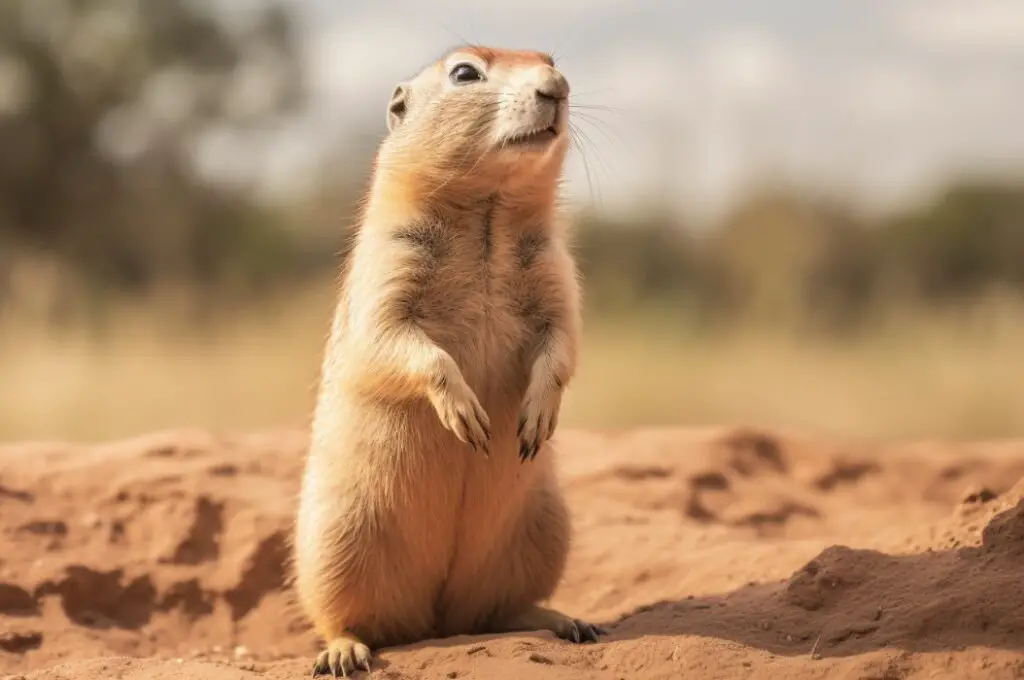

Prairie dogs are a great option to consider due to their similar physical characteristics and behavior patterns.
3. Ground Squirrels
Ground squirrels are small rodents that belong to the Sciuridae family. They are known for their burrowing behavior and share similar physical characteristics with groundhogs.
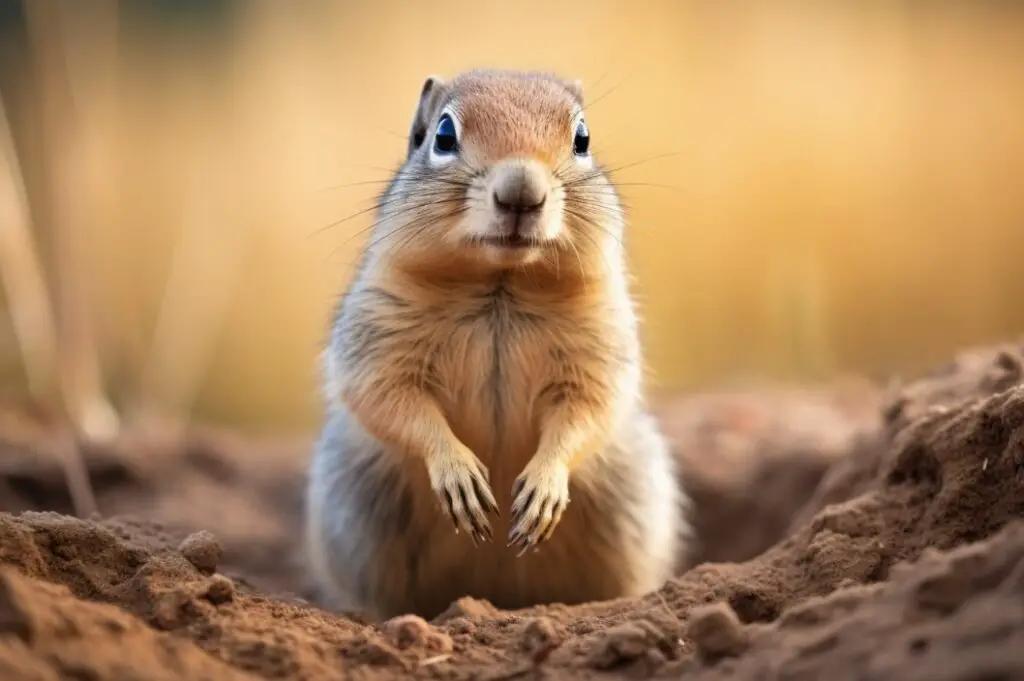

Here is a comparison of some popular species of ground squirrels:
| Species | Habitat | Size | Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| California Ground Squirrel | Western United States | 11-20 inches | Live in large colonies and dig extensive burrow systems. |
| Rock Squirrel | Southwestern United States | 8-11 inches | Active during the day and live in rocky areas. |
| Arctic Ground Squirrel | Arctic regions | 9-12 inches | Hibernate for long periods during the winter and build complex burrows. |
| Golden-mantled Ground Squirrel | Western United States | 7-10 inches | Often seen foraging for food and are not as active burrowers as other ground squirrels. |
| Siberian Chipmunk | Siberia and Northern Asia | 4-6 inches | Collect and store food in their cheek pouches and live in burrows. |
These ground squirrels have adapted to various environments and share characteristics such as short legs, strong claws, and white incisors. They use their strong claws for digging burrows and their short legs allow them to move quickly on the ground. Ground squirrels have fur-lined cheeks, which they use to carry food to their burrows.
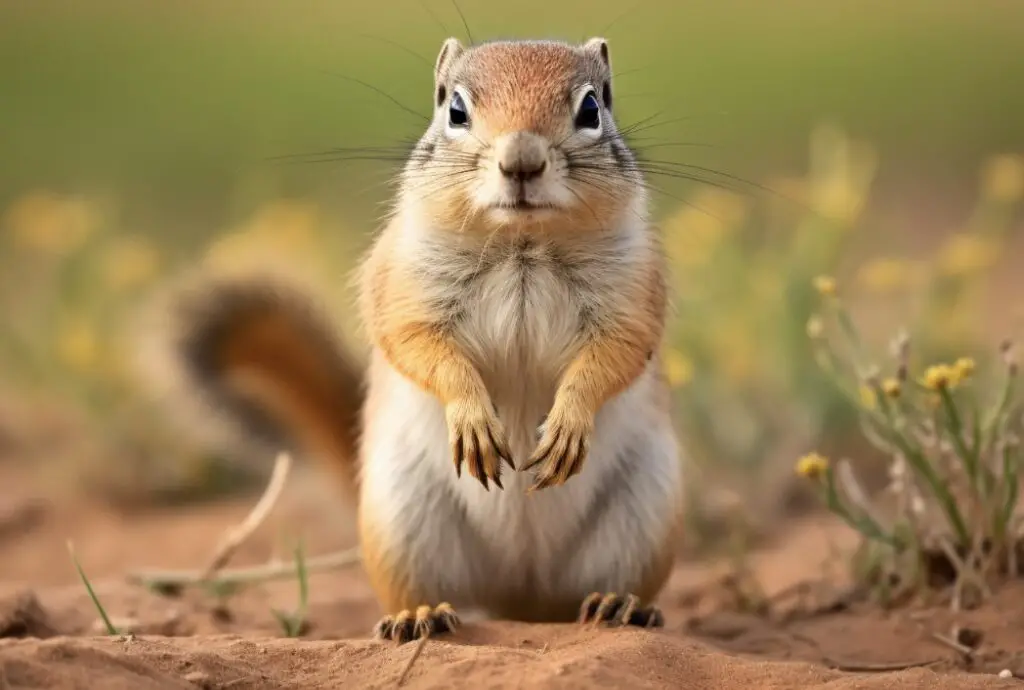

It’s important to note that while ground squirrels resemble groundhogs in some ways, they are distinct species with their own unique behaviors and characteristics. Understanding these differences can help you identify and appreciate the diverse animal life around us.
4. Gophers
To provide a comprehensive understanding of animals that resemble Groundhogs, it is important to explore the category of gophers.
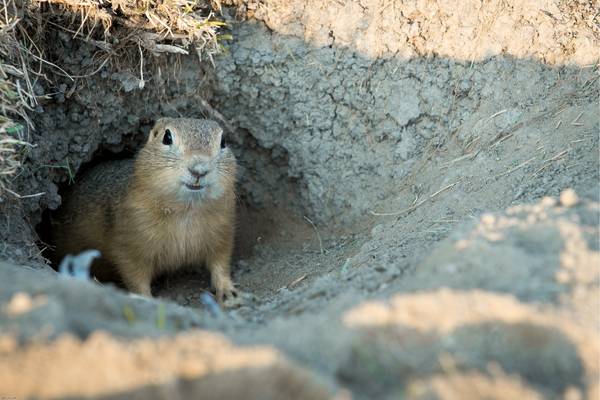

The following table gives information about gophers:
| Gopher Species | Physical Characteristics | Behavior Patterns |
| Pocket Gopher | Small, stocky rodents with short legs, stout bodies, and large cheek pouches | Gophers create extensive tunnel systems underground, which they use for foraging and protection. They are excellent burrowers. |
| Botta’s Pocket Gopher | Similar to Pocket Gophers, with characteristic pocket-like cheek pouches | They excavate burrows, creating complex tunnel systems. These gophers are known for their extensive burrowing behavior. |
| Thomomys Gophers | Range in size from small to medium, with short legs and fur-lined cheek pouches | Like other gopher species, Thomomys gophers dig elaborate burrow systems underground. They are solitary and territorial. |
Gophers, including the Pocket Gopher, Botta’s Pocket Gopher, and Thomomys Gophers, possess physical characteristics such as short legs, stout bodies, and distinctive cheek pouches. They actively dig burrows underground, creating complex tunnel systems that serve as their homes and provide protection from predators.
These animals are skilled at excavating, using their strong claws and incisors to dig through soil and create intricate networks of tunnels. Gophers are known for their burrowing behavior and rely on their underground dwellings for foraging and shelter.
Gophers are a group of rodents that share similarities with Groundhogs in terms of their burrowing habits and physical features. Their ability to dig extensive tunnels underground sets them apart and makes them a significant part of the animal kingdom.
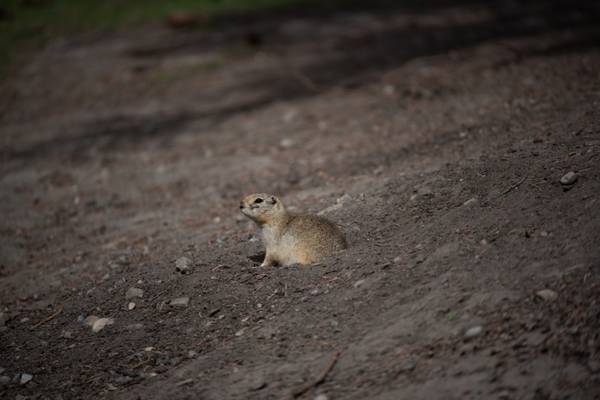

Gophers, widely found in North and Central America, have played a vital role in shaping ecosystems by aerating the soil and providing habitats for various other creatures. Their efficient burrowing techniques have been studied for their impact on soil composition and structure.
Gophers continue to be an intriguing species, constantly adapting to their surroundings in order to thrive in their underground habitats. Their survival skills and contribution to the environment make them a remarkable part of the natural world.
5. Susliks (European Ground Squirrels)
Susliks, commonly referred to as European ground squirrels, are small rodents predominantly found in Europe. They inhabit grasslands, pastures, and other open areas, often creating extensive burrow systems where they seek shelter and hibernate during the colder months.

While Susliks are similar in many ways to groundhogs, there are also distinct differences between the two species.
| Feature | Susliks (European Ground Squirrels) | Groundhogs |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Spermophilus (various species) | Marmota monax |
| Distribution | Predominantly Europe | North America |
| Size | Smaller, often around 20-30 cm in length excluding the tail | Larger, typically around 40-65 cm in length excluding the tail |
| Weight | Generally 200-350 grams | Typically 2-4 kg, but can be heavier |
| Lifespan | Around 5-6 years | Around 6-8 years |
| Habitat | Grasslands, pastures, open areas | Meadows, woodlands, open grassy areas |
| Burrowing | Extensive burrow systems, especially for hibernation | Extensive burrow systems, especially for hibernation |
| Diet | Omnivorous but predominantly herbivorous, consuming seeds, plants, and occasionally insects | Herbivorous, including grasses, fruits, and tree bark |
| Social Structure | Social, often live in colonies | Mostly solitary except during mating season |
| Hibernation | Hibernate during colder months | Hibernate during winter |
| Predators | Birds of prey, snakes, foxes | Foxes, coyotes, birds of prey, and humans |
| Conservation Status | Many species are under threat due to habitat destruction | Least Concern, but local populations may be threatened by human activity |
In summary, while Susliks and groundhogs share several similarities, particularly in their burrowing behavior and hibernation patterns, there are distinct differences in terms of size, weight, habitat preferences, and distribution.

Susliks are generally smaller, lighter, and more social compared to the larger, more solitary groundhogs. The conservation status of Susliks is also more concerning, with many of their habitats being threatened by human activities.
Animals that Share Similar Physical Characteristics with Groundhogs
Curious to discover animals that resemble the adorable groundhogs? Buckle up for an exciting journey into the realm of creatures that share uncanny physical traits with these furry fellows. From industrious beavers and playful nutrias to the unique capybaras, coypus, and chinchillas, each sub-section unveils fascinating facts and stunning resemblances that will surely leave you in awe. So, prepare to be amazed as we delve into a world of striking similarities and delightful discoveries!
1. Beavers
| Beavers | 1. Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents known for their exceptional dam-building abilities. |
| Appearance | 2. Beavers have brown fur, large webbed feet, and a flat, paddle-like tail. |
| Physical Characteristics | 3. Beavers have short legs, strong claws, and white incisors that continuously grow. |
| Burrowing Habits | 4. Beavers are proficient at digging burrows and constructing lodges using branches, mud, and stones. |
| Habitat | 5. Beavers are commonly found near bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, and ponds. |
Beavers, also known as large semiaquatic rodents, have several similarities with groundhogs. Beavers have a similar appearance to groundhogs, with brown fur and a flat, paddle-like tail. They also share physical characteristics such as short legs, strong claws, and continuously growing white incisors.

Like groundhogs, beavers are adept at digging burrows. They have excellent burrowing habits and can construct lodges using branches, mud, and stones. Their burrows serve as both shelter and protection from predators.
Beavers primarily inhabit areas near bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, and ponds. They are known for their exceptional dam-building abilities, utilizing their strong claws and teeth to manipulate their environment.
In summary, beavers resemble groundhogs in appearance, physical characteristics, and burrowing habits. They both thrive in habitats near water sources and play important roles in shaping their ecosystems.
2. Nutrias
Nutrias, which are aquatic rodents, bear a resemblance to groundhogs in some ways.

Here is a table providing information about nutrias:
| Nutrias | Physical Characteristics | Behavior Patterns |
| 2. Nutrias | 2. Large rodents with round bodies and short legs | 2. Excellent swimmers and spend most of their time in water |
| 2. Dense, coarse fur that ranges in color from brown to gray | 2. Build nests near the water’s edge using vegetation and mud | |
| 3. Long, orange incisors that continuously grow throughout their lives | 2. Active during the day and night, but more active at dusk and dawn |
Nutrias are native to South America and were introduced to various parts of the world for their fur. They are often found in freshwater habitats such as rivers, lakes, and marshes. The strong claws on their webbed hind feet make them excellent swimmers, allowing them to navigate through water easily.
Their fur-lined cheeks enable them to store food while they are underwater, and they mainly feed on aquatic plants. Nutrias are known for their ability to dig burrows in riverbanks, which serve as their nests and provide protection from predators.
Like groundhogs, nutrias are herbivores and play an essential role in maintaining wetland ecosystems. They can also cause damage to crops and flood-control infrastructure if their populations become too high.
Nutrias share physical characteristics such as round bodies, short legs, and dense fur with groundhogs. They exhibit behavior patterns such as building nests near water sources and being excellent swimmers. These aquatic rodents contribute to the diversity of wildlife in freshwater habitats while also posing challenges in certain environments where their populations need to be managed.
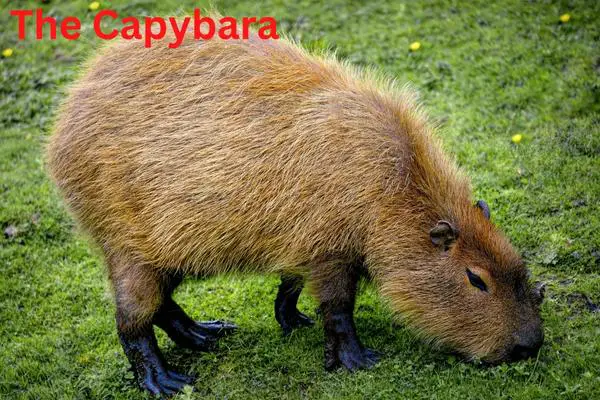
3. Capybaras
Capybaras, fascinating creatures, have several similarities to groundhogs.

Here is a list of characteristics that capybaras share with groundhogs:
- Herbivorous diet: Capybaras, just like groundhogs, are herbivores. They consume a diet mainly consisting of grasses, aquatic plants, and other vegetation.
- Social behavior: Both capybaras and groundhogs are social animals. Capybaras live in large groups, known as a “capybara community,” while groundhogs live in small family groups.
- Nocturnal habits: Capybaras, similar to groundhogs, are most active during the early morning and evening hours. They are known to rest and sleep during the hottest parts of the day.
- Excellent swimmers: Capybaras are known for their swimming abilities, just like groundhogs. They can use their large bodies and strong legs to navigate through water bodies with ease.
Fun Fact: Capybaras are the largest rodents in the world and can weigh up to 150 pounds (68 kilograms) on average.
4. Coypus
Coypus are large rodents that share similar physical characteristics with groundhogs.

Here is a table that highlights some key features of coypus:
| Characteristic | Description |
| Size | Coypus can grow up to 2.5 feet in length and weigh between 12 to 35 pounds. |
| Fur | They have coarse, brown or dark brown fur that is dense and waterproof. |
| Tail | Coypus have long, scaly tails that are similar to groundhogs but not as bushy. |
| Teeth | Like groundhogs, coypus have sharp white incisors that they use for gnawing on vegetation. |
| Legs | They have short legs with strong claws that are well-suited for digging burrows. |
| Behavior | Coypus are semi-aquatic rodents that are often found near bodies of water. They are skilled swimmers and can hold their breath for several minutes. |
Coypus, like groundhogs, play an important role in their ecosystems by contributing to the natural balance of their habitats. It’s worth noting that while coypus resemble groundhogs in certain aspects, they are different species with distinct characteristics and behaviors.

If you’re interested in observing animals that look like groundhogs, consider learning more about coypus and their fascinating features. Understanding the similarities and differences between these animals can enhance your appreciation for the diversity of the natural world.
Remember to respect and admire these animals from a safe distance, as they are wild creatures that should not be disturbed or approached closely.
5. Chinchillas
- Chinchillas: Chinchillas are small, furry rodents with bushy tails and short legs. They have fur-lined cheeks and strong claws. Chinchillas do not dig burrows like groundhogs, but they share similar physical characteristics.
- Marmots: Marmots are large rodents that are closely related to groundhogs. They have similar features such as bushy tails and short legs. Marmots are known for their ability to dig extensive burrows.
- Prairie dogs: Prairie dogs are small, social rodents that live in underground burrows. They have bushy tails, fur-lined cheeks, and short legs like groundhogs.
- Woodchucks: Woodchucks, also known as groundhogs, are the closest relatives to groundhogs. They share all the key physical characteristics, including bushy tails, fur-lined cheeks, and short legs.
- Ground squirrels: Ground squirrels are rodents that live in burrows and have similar physical features to groundhogs. They have bushy tails and short legs, but their fur-lined cheeks are less pronounced.
These animals may not be exactly like groundhogs, but they share enough similarities in appearance to be considered resemblances. Whether it’s their bushy tails, fur-lined cheeks, or short legs, these animals exhibit characteristics that are reminiscent of groundhogs.
Animals with Groundhog-like Behavior Patterns
If you’re fascinated by animals that exhibit similar behaviors to groundhogs, get ready to discover a variety of intriguing creatures.
From the social antics of meerkats to the elusive charm of bobcats, and even the mischievous nature of raccoons, this section will highlight animals with groundhog-like behavior patterns. Buckle up for an adventure exploring the intriguing world of animals that share traits and behaviors with these adorable rodents!
1. Meerkats
Meerkats, also known as suricates, are small mammals that belong to the mongoose family. They are native to the deserts and grasslands of southern Africa.
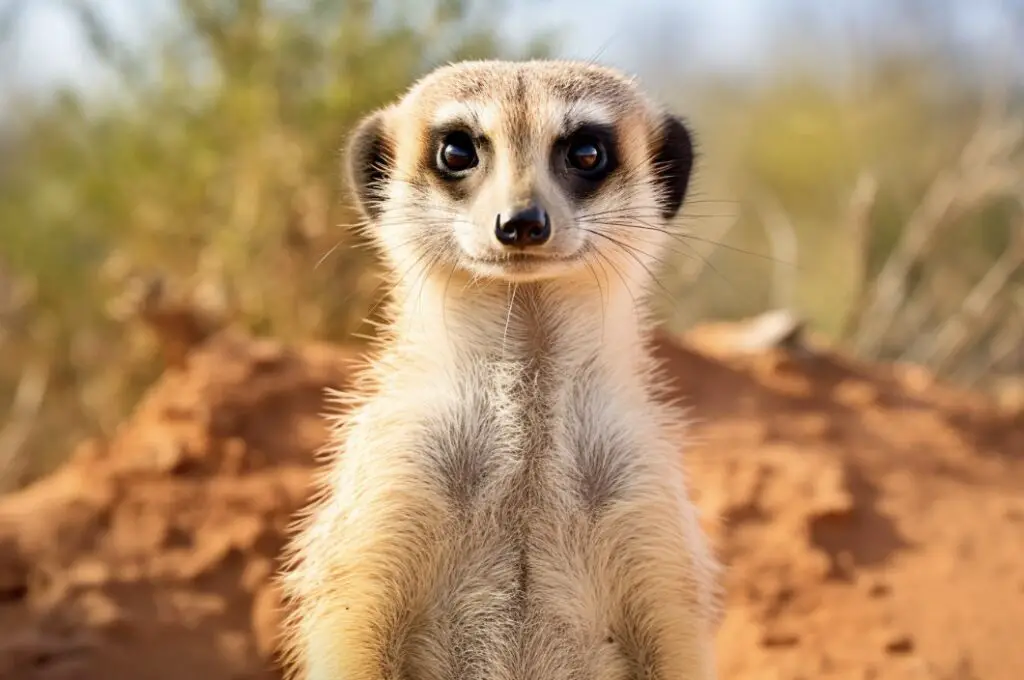

Here are some key characteristics and facts about meerkats:
- 1. Meerkats are highly social animals, living in large groups called mobs or clans. These groups can consist of up to 50 individuals.
- 2. They are known for their distinctive behavior of standing upright on their hind legs to keep watch for predators. This behavior provides them with a better view of their surroundings.
- 3. Meerkats have a slender body with a pointed nose and small ears. They have a longer tail compared to their body length.
- 4. Their fur is light brown to gray in color, with dark patches around their eyes. This helps to reduce glare from the sun while they are foraging.
- 5. Meerkats have strong claws on their paws, which they use for digging burrows. These burrows provide shelter from predators and extreme temperatures.
- 6. Their diet mainly consists of insects, such as beetles, spiders, scorpions, and small reptiles. They are also known to eat small mammals and birds.
- 7. Meerkats communicate through a variety of vocalizations, including growls, chirps, and a distinctive alarm call. This call is often described as a loud whistle, alerting the group to the presence of danger.
Meerkats are fascinating creatures that exhibit unique behaviors and adaptations for survival in their habitats. Their social nature and vigilant behavior make them fascinating animals to observe in the wild.
2. Tasmanian Devils
The following table provides information on the sub-topic “3. Tasmanian Devils”:
| Animal | Physical Characteristics | Behavior Patterns |
|---|---|---|
| Tasmanian Devils | Short legs, stocky build, dark fur with white patches on the chest and rump, sharp teeth | Solitary creatures, known for their aggressive behavior and loud vocalizations |
Tasmanian Devils, which are native to Tasmania, Australia, are small marsupials that share some physical characteristics with groundhogs. They have a stocky build with short legs, which allows them to move quickly and efficiently. Their fur is dark with white patches on their chest and rump, giving them a distinctive appearance.
In terms of behavior patterns, Tasmanian Devils are known for their solitary lifestyle. They establish territories and mark them with scent, defending their space from other individuals. They are also known for their aggressive nature, often engaging in fights over food or mates. When threatened or excited, they emit loud vocalizations, which can be heard from a distance.
Despite their similar physical characteristics, Tasmanian Devils are not closely related to groundhogs. They belong to the marsupial family and are the largest carnivorous marsupials in the world. Their diet consists mainly of carrion, small mammals, and birds.
While Tasmanian Devils may share physical characteristics with groundhogs, such as their short legs and stocky build, they have distinct behaviors and habitats. Studying these unique animals helps us better understand the diversity of wildlife across the globe.
3. Raccoons
Raccoons are animals that share similar behavior patterns with groundhogs. They possess several characteristics that make them resemble groundhogs.

- Raccoons, like groundhogs, are known for their ability to dig burrows. They create underground dens where they sleep and take shelter.
- These creatures also have bushy tails, which can help them with balance and communication.
- Similar to groundhogs, raccoons have fur-lined cheeks that they use to store food for later consumption.
- Both raccoons and groundhogs have short legs, which are adapted for their digging behavior.
- Raccoons have strong claws that enable them to climb trees and search for food.
- Like groundhogs, raccoons possess white incisors that they use for biting and chewing.
- Raccoons are known to produce loud whistles, especially during times of distress or when they feel threatened.
In the 1950s, raccoons were introduced to parts of Europe and Asia for their fur. Some of these raccoons escaped or were released into the wild, leading to the establishment of feral raccoon populations in these areas. Today, raccoons can be found in various countries outside of their native range, including Germany, Russia, and Japan. These adaptable creatures have successfully adapted to urban environments and can often be seen foraging for food in garbage bins or even entering people’s houses in search of a meal.
Remember to always keep a safe distance from raccoons in the wild and avoid feeding them, as they can become dependent on human food and lose their natural foraging abilities.
4. Badgers
- Badgers are animals that resemble groundhogs in some physical characteristics and behavior patterns.
- They are known for their ability to dig burrows, similar to groundhogs.
- Badgers also have short legs and strong claws, which help them in digging.
- Like groundhogs, badgers have white incisors that they use for gnawing and digging.
- Badgers have fur-lined cheeks, which they use to carry food and bedding materials to their burrows.
- Unlike groundhogs, badgers have bushy tails.
- Badgers are known for their loud whistles, which they use to communicate with other badgers.
- In terms of behavior, badgers are solitary animals, much like groundhogs.
- They are nocturnal and prefer to spend their days in the safety of their burrows.
- Badgers are carnivorous and primarily eat small mammals like rodents and rabbits.
- They are skilled hunters and have a strong sense of smell, allowing them to locate prey underground.
These are some key characteristics and behaviors that make badgers similar to groundhogs.
- Badgers, like groundhogs, are animals that share some physical characteristics and behavior patterns.
- Badgers, similar to groundhogs, are known for their ability to dig burrows.
- Badgers also possess short legs and strong claws, aiding them in their digging activities.
- Similar to groundhogs, badgers have white incisors which they use for gnawing and excavation.
- Badgers utilize their fur-lined cheeks to transport food and bedding materials to their burrows, just like groundhogs.
- Unlike groundhogs, badgers have bushy tails.
- Badgers are recognized for their loud whistles, which serve as a means of communication among fellow badgers.
- Regarding behavior, badgers, similar to groundhogs, are solitary creatures.
- They are nocturnal animals, preferring to spend their days in the safety of their burrows.
- Badgers, being carnivorous, primarily feed on small mammals such as rodents and rabbits.
- They are skilled hunters and possess a strong sense of smell, enabling them to locate underground prey.
These are some key characteristics and behaviors that make badgers similar to groundhogs.
5. Potoroos
Potoroos are small marsupials native to Australia, reminiscent of a cross between a rat and a kangaroo. They belong to the macropod family, which also includes kangaroos and wallabies. Potoroos have a keen sense for digging and foraging, often rooting around in the underbrush searching for fungi, their primary diet.

Groundhogs, on the other hand, are large rodents from North America, also known as woodchucks. They belong to the squirrel family and are perhaps best known for their burrowing habits and hibernation during winter.
While both animals have some digging habits and spend time foraging on the ground, they have distinct differences due to their taxonomic classifications, habitats, and lifestyles.
Table of Differences and Similarities
| Attribute | Potoroo | Groundhog |
|---|---|---|
| Taxonomic Class | Marsupial | Rodent |
| Diet | Primarily fungi, but also tubers and insects | Mostly herbivorous (grasses, plants, tree bark) |
| Size | Around 1 to 2.5 kg | 2 to 4 kg (can be larger) |
| Habitat | Forests and woodlands of Australia | Open fields, grasslands, woods in North America |
| Locomotion | Hopping, using strong hind legs | Quadrupedal, walks on all fours |
| Lifespan | Typically 5-6 years in the wild | 2-3 years in the wild, up to 6 in captivity |
| Burrowing Behavior | Digs shallow foraging pits | Digs deep, extensive burrows for shelter & hibernation |
| Social Structure | Solitary or in small family groups | Generally solitary except during mating season |
| Reproduction | Marsupial pouch; gives birth to undeveloped young | Gives birth to more developed young; no pouch |
This table provides an overview of the similarities and differences between potoroos and groundhogs, revealing their unique adaptations to their respective environments and lifestyles.
6. Aardvarks
Aardvarks
The aardvark is a unique mammal native to Africa. It is nocturnal and is best known for its diet of ants and termites. The name “aardvark” is Afrikaans for “earth pig,” and while its name might suggest a pig-like creature, its closest living relatives are actually elephants.

Aardvarks possess a long snout used to sniff out their prey and large, shovel-like claws designed for digging. Their burrowing behavior creates underground tunnels that serve both as homes and as a method to access their food sources.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Aardvark | Groundhog |
|---|---|---|
| Native Region | Africa | North America |
| Diet | Ants and termites | Grasses, fruits, and vegetables |
| Activity Cycle | Nocturnal | Diurnal |
| Burrowing Behavior | Create underground tunnels to find food | Dig burrows for hibernation and shelter |
| Physical Appearance | Long snout, large ears, shovel-like claws | Stocky body, short legs, strong claws |
| Family | Tubulidentata (related to elephants) | Rodentia (related to squirrels, rats) |
| Predators | Lions, leopards, hyenas | Foxes, coyotes, birds of prey |
| Lifespan (in the wild) | 7-10 years | 6-8 years |
While aardvarks and groundhogs both share the behavior of burrowing, they differ vastly in diet, native region, and evolutionary lineage.
Some Facts About 30 Animals That Look Like Groundhogs:
- ✅ Groundhogs have several interesting relatives that share similar appearances and behaviors.
- ✅ Marmots are the closest relatives of groundhogs and belong to the same squirrel family.
- ✅ Prairie dogs are another group of groundhog cousins found in the grasslands of North America.
- ✅ Beavers, known as “nature’s engineers,” are hard-working and industrious groundhog cousins.
- ✅ These animals have unique characteristics and behaviors that set them apart from groundhogs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some animals that look like groundhogs?
Some animals that resemble groundhogs include marmots, badgers, beavers, capybaras, and chipmunks.
How can you distinguish the Alaska marmot from a groundhog?
The Alaska marmot can be identified by its longer tail and darker fur compared to a groundhog.
Where can the alpine marmot be found?
The alpine marmot is found in the Tatras and Northern Apennines, mountainous regions in Europe.
What are some distinct characteristics of badgers compared to groundhogs?
Badgers are larger than groundhogs, have black-and-white striped fur, and primarily feed on small mammals.
How do beavers differ from groundhogs?
Beavers are much larger than groundhogs, have a flat tail, and are known for their ability to build dams and lodges.
What similarities do black-capped marmots share with groundhogs?
Black-capped marmots, though smaller in size, are also members of the squirrel family and dig burrows for shelter, similar to groundhogs.