Fish come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and most are either carnivores or herbivores but few feed entirely as scavengers! In the wild fish mainly eat algae, worms, plankton, and each other (!) but some species of fish are opportunistic feeders that will eat anything they can get hold off.
Most fish are not scavengers, but there are a few species that will mainly feed on dead or dying animals. These scavenger fish include the hagfish, lampreys, remoras and a few shark species. As well as some bottom-dwelling fish like catfish, eels, and eelpouts that will also scavenge for food as their main food source.
As scavengers, fish consume dead and decaying organic matter that would otherwise pollute the water or take ages to decompose.
Scavenger fish, like catfish or lampreys, help to break down this organic matter much faster into simpler compounds that can be more rapidly be used by other organisms in the ecosystem.
Contents
Habitat and Diet of Scavenger Fish
Fish that feed as scavengers are found in both freshwater and saltwater habitats.
Like all fish, scavenger fish are cold-blooded, meaning that their internal temperature changes with the surrounding water temperature, but scavenger fish tend to be found in the warmer, tropical waters of the world.
Scavenger fish are mostly carrion eaters, which means that they eat the carcasses of other animals.
Some opportunistic scavenger fish are also filter feeders, which means that they strain small organisms and dead or decaying plant and animal matter out of the water to eat them.

Scavenger fish are mostly carnivores but they may eat a wide variety of organisms, from plankton to plants and animals. Depending on the type of scavenger fish, they primarily eat other fish, small aquatic invertebrates such as molluscs (like squids and octopuses) and crustaceans (crabs and lobsters for example), and even whales and sea birds!
In general, scavenger fish will eat:
Dead or dying fish.
Dead snails or slugs.
Dead octopuses or squids.
Dead sharks.
Dead sea cucumbers.
Dead crustaceans including crabs and lobsters.
Birds that fall into the water.
Dead mammals (seals, whales, sea lions, polar bears).
Their exact diet of scavenger fish changes between seasons, as different food types become more abundant and animals die more or less frequently.
But also during their lifetime as they grow bigger and can handle larger food items and are able to deter other scavengers like crabs or lobsters from a popular carcass that was not available to them as juvenile scavengers.
What Fish are Considered Scavengers?
Whereas most fish species do not eat dead animals as a major part of their diet, there are a few groups of fish scavengers that get most of their nutrients through fish carrion or detritus.
These primary scavenger fish are:
- Catfish
- Sharks
- Hagfish
- Lampreys
- Remoras
- Eels
- Eelpouts
But keep in mind that these scavengers are just a small portion of all the decomposers and scavenger animals found in the ocean!
Catfish
Catfish are scavengers that feed on dead and decaying matter at the bottom of primarily lakes, rivers, and other freshwater habitats.
They use their sensitive barbels (whiskers) to detect food in the water and then vacuum it up with their mouths. Catfish are important members of the aquatic food web because they help clean up these habitats by consuming decomposing matter.
Many people know catfish from their aquarium where some Plecostomus species (also known as pleco fish) like the Suckermouth catfish are kept as pets. This catfish belong to the Loricarioidea family of catfish that are all scavengers.
Loricarioidea catfish
There are over 60 species of fish within the family Loricarioidea, also known as armored catfish.
These fish are native to freshwater habitats in South America, and get their name from the bony plates that cover their body.
Armored catfish vary in size, with some species reaching over a foot in length, and are typically brown or grey with stripes or dots in coloration.
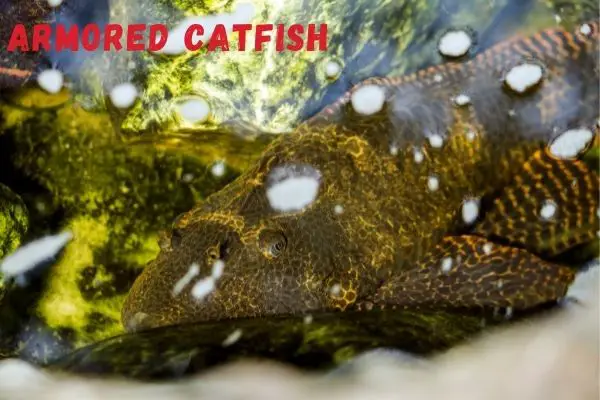

Most species are bottom-dwellers, and use their large mouths to vacuum up food from the substrate and will stop to gulp on dead animals. Some armored catfish are popular aquarium pets, but many others are harvested for food.
These freshwater catfish species are effective in cleaning the bottom from dead plant and animal material and also rinses the glass of a fish tank with their suction-cup mouths!
Corydoras catfish
Corydoras fish, also known as Cory Catfish, are treasured aquarium pets due to their small size and efficient cleaning behaviour!
Corydoras are a type of armored catfish that scavenge the bottom of freshwater tanks and ponds for food. These bottom feeders are native to tropical regions of South America and typically live in slow moving or standing waters.
Corydoras have a unique set of barbels around their mouths that they use to help them find food in the substrate. These barbels are also very sensitive and can detect changes in water pressure, temperature, and vibration.
This allows Corydoras to be able to sense when predators are nearby or when there is potential danger in their environment.

While Corydoras are mostly scavengers, they will also consume plant detritus, small insects, and other organic matter that they find on the bottom of their tank or pond.
Most of the time, these small catfish will find dead fish on the bottom and eat them, but if it notices that anything else is already eating the fish, it may skip out if it feels threatened.
Saltwater (marine) catfish
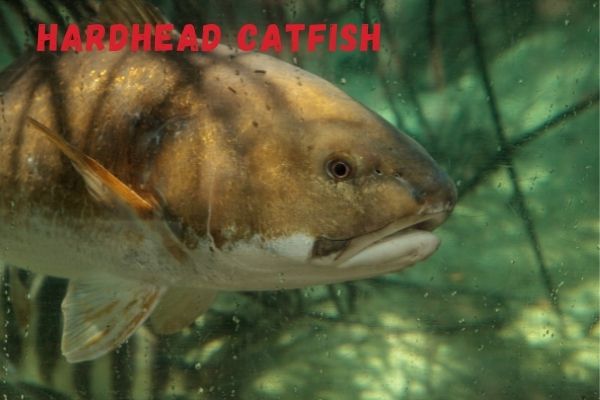
Most scavenging catfish are found in tropical freshwaters such as fast flowing stream, but some catfish like the gafftopsail catfish and the hardhead catfish live in the saltwater of the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf.
These two saltwater species, however, are not primarily scavengers as they also eat living prey and the latter species also eats algae and plants.
This is true for other catfish as well and although the catfish is called a scavenger, it is also an omnivore, eating both plants and animals, but the major part of its diet will be consumed as carrion.

The next fish type on the list, however, will not usually hold back when any type of flesh is within sight!
Scavenger Sharks
Whereas many sharks are not thought to actively seek out dead animals as scavengers, most of them will not leave carcasses untouched for long – especially if short on living food.
Sharks are also opportunistic feeders and will eat meat that’s either dead or dying, including dead or dying fish, whales, seals, dolphins, seabirds, turtles, and other sharks.
However, some sharks are known to behave more as scavengers than others and are better known of the kind is the Greenland shark.
Greenland shark
The Greenland shark is a true scavenger of the sea. It feeds on seals, fish, and even whales that have died and sunk to the ocean floor.
Greenland sharks are large, slow-moving scavengers that live in the cold waters of the Arctic and North Atlantic oceans. These sharks are mostly found in deep waters, where they feed on the carcasses of other animals that have sunk to the bottom.
Despite their size and slow movement, Greenland sharks are very difficult to study in the wild. They are rarely seen by humans and much of their behavior and ecology is largely unknown.

What we do know, however, is that Greenland sharks are one of the few species of shark that can live in water temperatures below 0 degrees Celsius (32F). This makes them well-adapted to a life in the Arctic.
Like other sharks, the Greenland shark has a great sense of smell that helps it find food.
And although the Greenland shark is one of the slowest-moving sharks in the ocean, but as a scavenger it doesn’t need to swim fast to catch its dinner!
Another reason why the Greenland shark is definitely not in a hurry is its long average lifespan of around 350 years!
The Great White Shark
Great white sharks are the largest predatory fish in the world. They are apex predators and have no natural enemies. They generally feed on a variety of animals including other sharks, seals, dolphins, whales, seabirds, fishes, squid, and turtles.
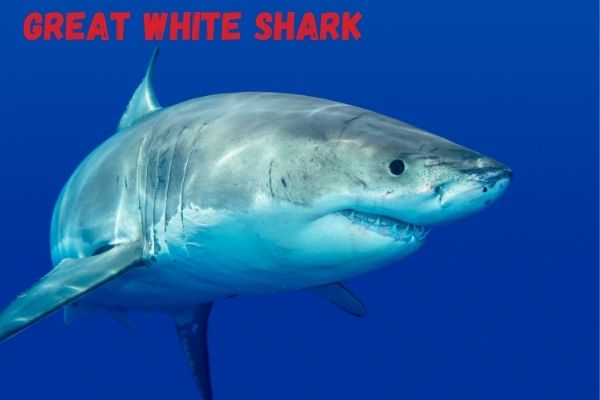

The great white shark was long thought not to scavenge for food, but a scientist reveals that it actually eats carrion as part of its diet.
In a recent study the researchers present findings from multiple observations of white sharks scavenging on whale carcasses in False Bay, South Africa.
The main author of the study said:
Great white sharks normally feed on dead whales, which are important food resources for the solitary predators. During such a feast, when one shark accidently bit another on the head and left two teeth behind, the other sharks showed no aggression toward the biter.
Neil Hammerschlag
This indicates that scavenging is part of the social behaviour of white sharks.
Tiger Shark
Like the Great White Shark, Tiger sharks are one of the most feared predators in the ocean. But what do these massive creatures actually eat? Spoiler: They are very similar to the White Shark!
The tiger shark is a part time scavenger, which means that it occasionally feeds on the remains of other animals.
They will also eat live prey, but this only makes up a small part of their diet. Carcasses are their preferred food, and they will often swim long distances to find one.
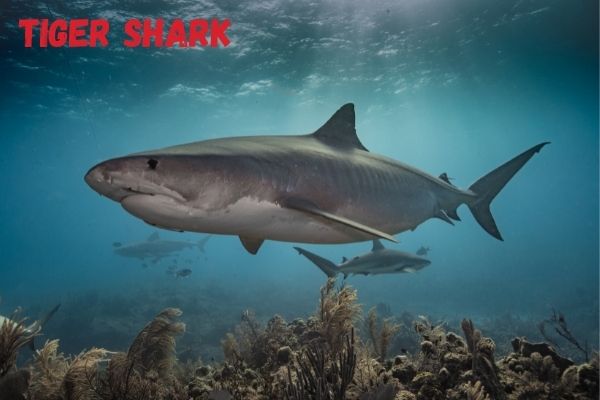

Tiger sharks have been known to eat just about anything, including turtles, dolphins, birds, and even other sharks. If it’s dead and in the water, there’s a good chance a tiger shark will try to eat it!
Hagfish
Hagfishes are bony fish that are not closely related to other fish except the lampreys.
Hagfish are scavengers, eating dead or dying animals. They scavenge and feed on dead fish, dead squid, dead seabirds, dead whales, dead other hagfish and dead sharks.
They are opportunistic feeders, which mean they will eat anything they can get. They are known to take on even the largest of carcasses where they will sometimes just dig a tunnel through the flesh as they are eating!
The stomach of a hagfish has a very strong acid that can dissolve most things. Hagfish can survive and function without food for up to 12 months.
They are mostly found in coastal waters and are considered passive scavengers. They will eat just about anything. They have eyes like other fish but their sense of smell is more developed as they have a nose more like a terrestrial animal.
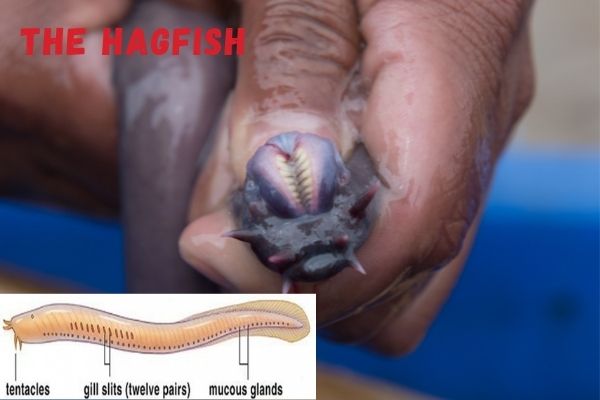
Hagfish live in the deeper and darker parts of the ocean and their eyes are barely functional, but their sense of smell is quite developed.
This is in contrast to their sister species, the lampreys, that have fully functional eyes and a more well developed brain function to process the visual inputs.
Lampreys
Lampreys are grey, eel like fish that have a toothed tongue and like the hagfish, they are ancient creatures without jaws that resemble a mix between worms and fish.
They are one of the oldest and most primitive types of vertebrate and have been around for almost 450 million years.
Lampreys are prominent scavengers of the sea and they feed on anything they can find. They eat dead and decaying fish, sharks, whales, other mammals, octopuses and squid.
They feeding habits are quite similar to that of hagfish but lampreys are also known for feeding by attaching their toothed tongue to their prey as they chew through.
With their round mouth full of sharp teeth, lampreys look like something coming out of a sand dune in a science fiction movie, and they almost behave accordingly in real life!
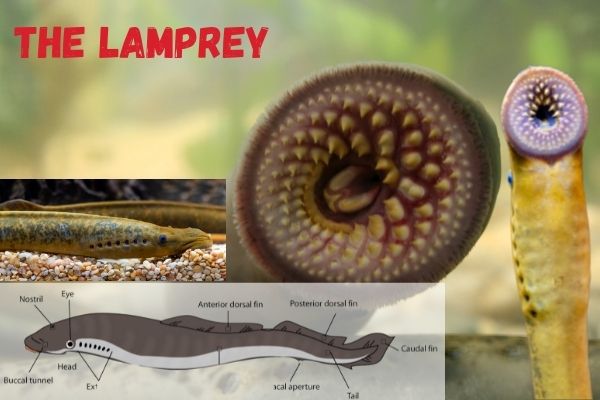

Lampreys are closely related to hagfish, but they do differ in some important aspects. Lampreys bodies are less eel like compared to hagfish and they tail fins are more developed.
Their mouths are more defined, round and full of sharp visible teeth around the moth opening as well as on their tongue.
Eels
Eels live in almost every type of aquatic habitat, from the poles to the tropics. They can be found in freshwater, brackish water and salt water. Like Salmon, eels are catadromous, meaning they live most of their life in the ocean, but migrate to fresh water to breed.
Some eels are scavengers, and will feed on many different food items throughout their lifetime. They eat other fish, crabs, worms and other small animals.
The snubnosed eel is a good example of a scavenging eel. They are scavengers because they eat the carcasses of other animals, but they may also attach themselves to bodies of larger fish and sea mammals to feed on their blood!
Eels are important to the food chain because they are both a predator and prey to many other aquatic animals.
Eelpouts
Eelpouts are eel-like scavengers that help clean up the ocean floor by eating dead and decaying plants and animals.
Eelpout live on the bottom of the ocean, at depths around 200 meters. Like other scavengers, they are opportunistic feeders and eat whatever they can find.
In the wild, they mainly feed on dead animals that fall from the surface, but also algae, fish eggs, small crustaceans and carcasses of any type of animal.
Eelpouts are not considered decomposers, as they do not break down the organic material into smaller parts. Instead, they use special bacteria in their digestive system to break down the food. This bacteria is acquired when the eelpout eat other bacteria and algae.
One example of an eelpout is the viviparous eelpout (Zoarces viviparus) that is a species of fish in the family Zoarcidae. It is found in marine waters off northern Europe and the Mediterranean Sea.
The viviparous eelpout is a scavenger, feeding on small crustaceans, worms, molluscs, and dead fish.
Remoras
The remora is a tiny fish that feeds mostly as a scavenger. It feeds off of the scraps and remains of other fish.
Like lampreys, it uses its suction-like mouth to attach itself to larger fish and then picks at their skin and scales, eating whatever it can find. The remora is not a parasitical fish, as it does not live off of the host’s blood or body, and may actually be considered beneficial to some hosts.
Remoras are one of the few animals that have an almost symbiotic relationship with sharks. The remora attaches itself to the shark with a suction cup on the upper part of its body – practically on its head!
The remora attach to sharks so that it can feed off of the scraps that the shark leaves behind after eating, but also because it gains protection and saves energy on transportation!
In this way, the remora acts as a scavenger, cleaning up after the shark and helping to keep the shark free of (other!) parasites.
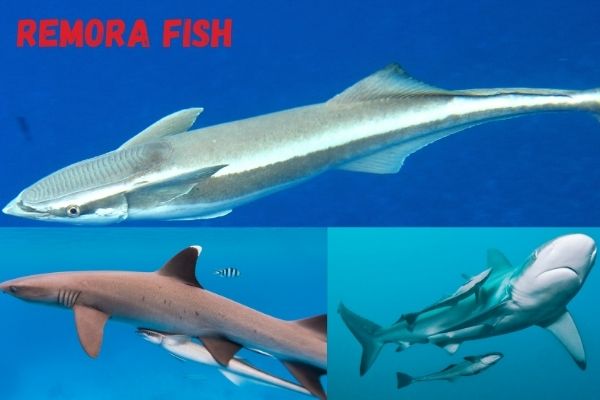

In return, the remora keeps the shark clean and eats other parasites on the shark.
They can be found attached to sharks, turtles, ships, whales, and dolphins. They attach themselves by suction and feed on food scraps that float by. They eat dead skin, scales, mucus, and parasites from larger animals.
They drift along in the water carried by currents and waves until they encounter a new host or a carcass to feed on.
Are any small fish scavengers?
Most scavenger fish are larger fish, but there are some species of catfish that are quite small like the Otocinclus catfish, the Pictus Catfish or the Asian stone catfish.
Otocinclus catfish
Otocinclus catfish are scavengers that live at the bottom of freshwater tanks and bowls. They are opportunistic feeders that will eat anything they can get, including dead plants and animals, algae, and detritus.
However, otocinclus catfish are not as much animal scavengers as they are plant scavengers and they will mostly eat dead plants and algae.
Pictus Catfish
The Pictus catfish is a freshwater fish that is native to South America. The fish gets its name from the Latin word “pictus” which means “painted”. This refers to the distinct markings on the body of the fish. The Pictus catfish is also known as the Pimelodus pictus, the Leopard Corydoras and the Polka Dot Corydoras.

The Pictus catfish is a scavenger that feeds on detritus, small insects, crustaceans and other small aquatic creatures.
The diet of the Pictus catfish changes as it grows older and larger. Adult fish have been known to eat smaller fish and even tadpoles
Asian stone catfish
Asian stone catfish are scavengers that live in freshwater environments. They are small fish that feed on a variety of food items, including dead and decaying plants and animals.
They help to break down organic matter and make it available for other organisms in their environment. This process is important for keeping freshwater ecosystems such as those in fish tanks healthy and balanced.
Doctor Fish
Other fish, such as the well-known “doctor fish”, or Garra rufa, that eat off skin cells from peoples feet, can be considered scavengers as well.
Garra rufa is a species of freshwater fish that feeds primarily on dead organic matter. These small, reddish-brown fish are native to the rivers and streams of Turkey and Central Asia, but they have been introduced to many other countries for use in aquaculture and spa treatment facilities.
While garra rufa are technically carnivores, they scavenge the majority of their food. In the wild, they will eat anything from detritus to insects to small vertebrates.
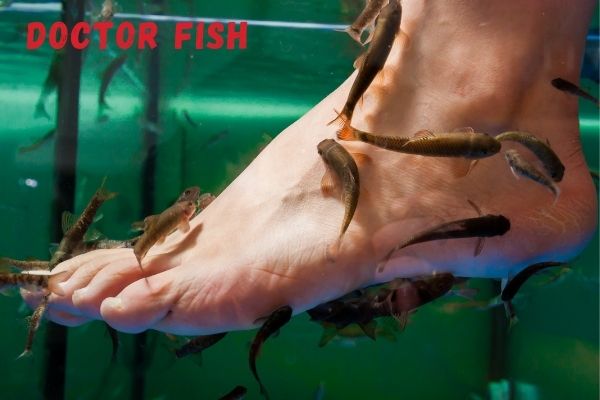

However, in human captivity their diet consists mostly of dead skin cells shed by our feet! They have rows of tooth-like structures called “dermal denticles” that help them scrape off this food source.
Garra rufa are sometimes used as a form of alternative medicine, as their feeding habits can provide relief for people with certain skin conditions like psoriasis or dermatitis. However, there is no scientific evidence to support these claims.
What are some fish that are not scavengers?
Most fish in the oceans, streams and rivers are not considered scavengers as they predominantly eat living things.
Are flounders Scavengers?
Flounder are mainly predator fish and not scavengers. Flounders will hunt for smaller fish near the bottom of the ocean. Their diet consists mostly of other fish, but they also eat squid, shrimp, and crabs.
Flounders are carnivores, meaning that their diet is based on eating other animals. This is different from an omnivore, which eats both plants and animals.
Flounders tend to be bottom feeders, which means that they eat small fish and invertebrates that live near the seafloor.
Flounders are ambush predators, meaning that they lie in wait for their prey to swim by before attacking. This makes them difficult to see since they blend in with the seafloor. When a flounder sees its prey, it will open its mouth wide and suck the prey in whole.
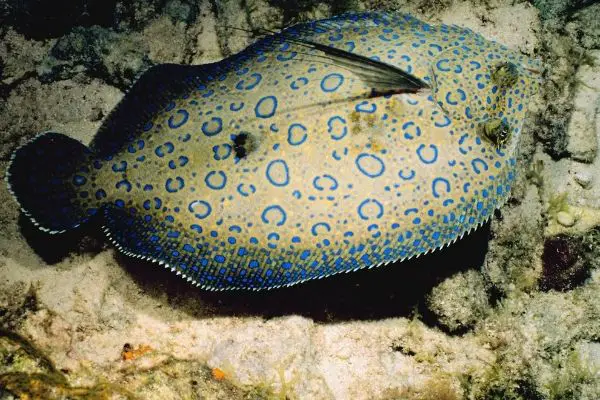

However, flounders will prey on animals that are already dying or dead but flounders prefer to eat living animals and eggs. Flounder will occasionally eat dead shellfish as well.
Is a Monkfish a Scavenger?
No, monkfish are not primary scavengers as they prefer living prey. Monkfish are predators that hunt on the bottom of the sea. In the wild, they form an important part of the food web since they eat a wide variety of fish, mollusks and crustaceans,
Monkfish are not scavengers but can function as carnivores in the ocean. Whereas they mostly eat living things like other fish, monkfish will not let a good carcass go to waste, but it is not their main way of feeding!
However, true scavengers are the bacteria and fungi that live in the monkfish’s digestive system and perform the final steps of digestion.
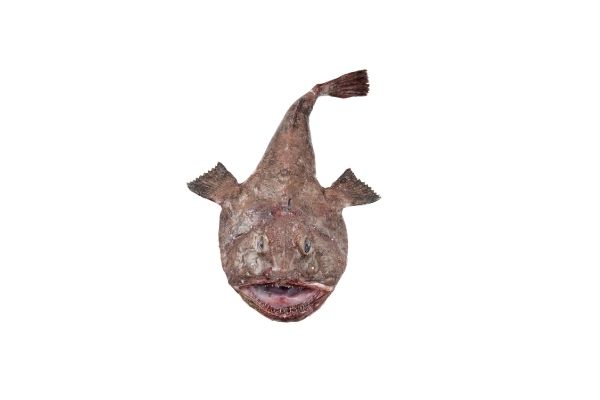

Monkfish are opportunistic feeders that will eat anything they can get. In the wild they mainly eat shrimp, crabs, worms, plankton, carrion and smaller fish.
Their diet changes between seasons, as different food types become more abundant, or as they grow bigger and can handle larger food items like other fish.
Are Betta Fish Scavengers?
No. Betta fish are carnivores and will eat other fish. They will usually not scavenge or eat dead animals. Betta fish can be trained to eat plant matter as well.
Betta fish are beautiful, unique creatures that make a great addition to any aquarium. But be careful, although they are small, they have a voracious appetite and will eat just about anything that fits in their mouths.
Bettas are carnivores, meaning that their diet consists mainly of meat. In the wild, they feed on small insects, crustaceans, and other invertebrates. Bettas also consume plant matter on occasion, but this is not necessary for their survival.

In captivity, bettas can be fed a variety of foods including pellets, freeze-dried shrimp, live food such as brine shrimp or bloodworms, and even vegetables like blanched spinach or zucchini. It is important to offer your betta a varied diet to ensure that they are getting all the nutrients they need to stay healthy and happy.
Is a Sea Bass a Scavenger?
No. Sea bass are predators and not scavengers. They have very large mouths with big teeth. They are predatory fish which mostly eat fish, crabs, shrimp, and squid. They have been seen to eat small seabirds too.
Sea bass are carnivorous fish that are found in the open ocean. They are predators that hunt smaller fish, squid, and crustaceans. Sea bass have a large mouth with sharp teeth that they use to tear their prey apart.
Sea bass are an important part of the marine ecosystem as they help to keep populations of other animals in check. However, due to overfishing, the population of sea bass has declined in recent years. This is a problem because it can lead to an increase in the populations of their prey, which can then have a negative impact on the ecosystem as a whole.
Is Whiting Fish a Scavenger?
No. Whiting fish are predators and not scavengers. The whiting is a carnivore, with adults feeding mostly on crabs, squids, octopus, shrimps, worms, and several other small invertebrates.
Whiting fish are small, silver-colored fish that are found in the ocean. They have a long, slender body with a forked tail. Whiting fish are omnivorous, which means they eat both plants and animals.
Whiting fish play an important role in the ocean ecosystem. They are a food source for larger predators, such as sharks and dolphins. They also help to control the population of smaller prey animals by eating them.
Is Halibut a Scavenger Fish?
No. Halibut are predators, not scavengers. Halibut feed on small fish, shrimp, crabs and jellyfish, and are known to feed on dead animals.

Halibut are bottom-dwelling carnivorous fish found in the North Atlantic and North Pacific Oceans. They are flatfish, meaning they have both eyes on one side of their body. Halibut can grow to be very large, with the biggest on record weighing in at over 500 pounds!
Halibut are predators and eat other fish, squid, shrimp, and crab. Their diet depends on what is available in their environment, but they typically prefer smaller prey. Halibut use their sense of smell to locate food and will bury themselves in the sand or mud to ambush their unsuspecting prey.
Is mackerel a scavenger fish?
Mackerel is a carnivore with adults feeding mostly on small fish, crabs, squids, octopus, shrimps, worms, and several other small invertebrates.
This means that they do not eat dead animals by that the vast majority of the mackerels diet is composed of other animals. In fact, mackerel can consume up to ten times their own body weight in food each day!
While the vast majority of their diet is made up of other fish, mackerel will also consume squid, shrimp, and crab when available.
Are goldfish scavengers?
Yes. Goldfish can actually be scavengers. Wild goldfish primarily eat plants, insects, crustaceans, and small fish. But goldfish will occasionally eat dead plants.
In captivity, their diets are usually supplemented with prepared flake foods, frozen brine shrimp, bloodworms, tubifex worms, and other commercially prepared foods.
Goldfish also consume decaying matter in a pond, such as dead plants. However, goldfish do not eat decomposing animal matter.
While goldfish will eat just about anything, it’s important to give them a well-rounded diet that includes both plant and animal matter.
Are Cod Fish Scavengers?
No. Cod do not eat dead animals. Cod are carnivorous fish that live in the open ocean. In the wild, they feed on a variety of smaller fish and invertebrates. Their diet changes as they grow, with larger cod feeding on larger prey.
Wild cod eat a variety of animals including mollusks, (like mussels and clams), crustaceans, (like shrimps and crabs), and cephalopods, (like squid and octopus). Cod also eat small amounts of algae and plankton.
Cod are an important food source for humans, and have been harvested for centuries. They are a popular choice for seafood lovers because of their mild flavor and firm texture.
Are Tuna Fish Scavengers?
No, tuna are not scavengers. They are predators. Tuna mainly eat other fish and squid.
Tuna are one of the most popular fish in the world, and they’re also one of the most carnivorous. Tuna are predators that hunt other fish, squid, and crustaceans.

Their diet is relatively high in fat, which helps them stay buoyant in the water and gives them energy to swim long distances.
Is a Salmon a Scavenger?
No. Salmon are omnivores. In the ocean, salmon will feed on small fish, krill, and shrimp. However, salmon are typically farmed in captivity, where they are fed pellet food made from soy and dried fish.
Salmon are an important food source for many animals in the wild, including bears, eagles and other fish. They are also a popular food choice for humans, as they are a nutritious and healthy option.
Are Buffalo Fish Scavengers?
No. Buffalo fish are predators, not scavengers. They are omnivores, which means they will eat both plants and animals. They are freshwater fish that are native to North America.
Adults eat mostly small fish, but they also eat insects, mollusks, and crustaceans. Young buffalo feed on algae and other microorganisms in the mud at the bottom of streams and lakes.
Are Guppies Scavengers?
No. Guppies are omnivores and not scavengers. Guppies eat small aquatic crustaceans, insects, worms and plant matter.
Guppies are a type of freshwater fish that are native to Trinidad and Tobago. These brightly colored fish are popular among aquarium enthusiasts and can be found in many pet stores. Guppies are omnivores, which means they will eat both plants and animals.
In the wild, guppies eat a variety of small invertebrates, such as brine shrimp, mosquito larvae, and small crustaceans. They also consume algae and other plant matter.
Is Tilapia Fish Scavengers?
No. Tilapia are not scavengers, but they are partly detritivores which means that their diet contains a bit of decaying organic matter.
However, they are mostly herbivores and in the wild, tilapia eat algae, aquatic plants and to a lesser extend insects, crustaceans (like crayfish), and other small fish.
Are Swai Fish Scavengers?
No. Swai fish are not scavengers, but they are omnivores meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
Are bonefish scavengers?
Bonefish are not scavengers but omnivore predators. Bonefish are opportunistic feeders that will eat anything they can get. In the wild they mainly eat algae, shrimp, worms, plankton, carrion and fish.
If you are more interested, I have written a whole article about the diet of bonefish.
Their diet changes between seasons, as different food types become more abundant, or as they grow bigger and can handle larger food items like other crustaceans.
Are opaleye fish Scavengers?
Opaleye fish are not scavengers, but they will occasionally eat dead small invertebrates if they happen to come across them.
However, the vast majority of their diet consists of algae and other plant matter, which they graze on throughout the day.
If you want to know more, I have written more about the diet of Opaleye fish here.
Conclusion
We have gone over some of the most important fish that are scavengers. They will eat dead and decaying plant and animal matter that they find in the water.
This helps to clean up the environment and together with the decomposers found in water, they keep the marine and freshwater environments healthy.
Other decomposers and scavengers in the oceans are:
Click on each animal to read my in-depth descriptions of them and their role in the ecosystem!
As they are one of the most abundant vertebrate scavengers in the ocean, scavenger fish also eat the corpses of other animals, and often eat the leftovers of other fish.
This is a very important ecological role for them, as they help to regulate the amount of available food in the oceans, and prevent the depletion of food sources.
Scavenger fish and decomposers play an important role in the food chain, because they help to recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.




