Catfish are carnivores that mainly eat other fish. However, they are also scavengers and will eat just about anything they can find. This includes dead animals, insects, worms, and even smaller Catfish.
Catfish are tertiary consumers in the food web. This means that they are predators that eat other predators. In the wild, they are also scavengers that play an important role in keeping the freshwater ecosystem balanced and clean!
Catfish have a varied diet depending on their environment and what is available to them. In the wild, their diet consists mostly of other fish, but they will also eat insects, crustaceans, and mollusks if given the chance.
Catfish are a diverse group of predatory fish that inhabit freshwater (the word catfish itself refers to a group of fish that originated in the catfish family).
Most are solitary fish, but also include species that form schools, which can include very large numbers in the case of the Mekong giant catfish (see video below).
Catfish are voracious predators, feeding on a variety of animal matter, including aquatic insects, worms, other fish, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals. Over time, they have evolved many specialized traits, including:
- Sharp, protrusible barbells (whiskers) that aid in recognizing prey buried in the substrate.
- Sharp teeth that are easily replaced.
- Eyes capable of seeing in dim or even dark conditions.
- Strong jaws that are adapted for crushing hard food items, including hard-shelled mollusks.
- Gill rakers that comb through the substrate for additional food acquisition.
Catfish are members of the order Siluriformes (catfishes) in the family Ictaluridae (channel catfish). The group includes more than 1,500 species. Some catfish, such as plecos, are closely related to cichlids, which are another large and diverse group of fish.
Contents
Are catfish good for the ecosystem?
Catfish are important in the ecosystem for a variety of reasons. They are carnivores, scavengers, and tertiary consumers, which means they help to keep the populations of other animals in check.
They also help to clean up the environment by eating dead and decaying matter, which is one of the most important roles that catfish play is in the food chain
As tertiary consumers and scavengers, catfish help to control the populations of primary and secondary consumers.
This is because they eat both plants and animals, which helps to keep the numbers of herbivores and carnivores in check. In addition, their scavenging habits mean that they help to clean up the environment by eating dead and decaying matter.

Catfish are also an important source of food for humans. In many parts of the world, catfish is a staple food source, especially in Africa where it is often dried and smoked.
Catfish is a nutritious food that is high in protein and low in fat, making it a healthy option for people who want to lose weight or maintain their current weight.
Are Catfish Carnivores, Herbivores, or Omnivores?
Catfish are generally considered omnivores, meaning they have a diverse diet that includes both plant and animal matter. However, the specific diet of a catfish can vary depending on the species and its habitat.
Some catfish are pure carnivores others are herbivores or omnivores. Some smaller species are even limnivores that live off of microorganisms in mud.
Even purely carnivorous species may get plant matter in their gut because of the herbivore prey they ate, but this is consumed unintentionally.
In the wild, catfish are opportunistic feeders and will consume a wide range of food sources. They are known to eat small invertebrates such as insects, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms. They also feed on plant matter like algae and aquatic vegetation.
In captivity, catfish are often fed a combination of commercial fish pellets or flakes, which provide essential nutrients, and live or frozen foods like bloodworms, brine shrimp, and daphnia. Some catfish species, such as the popular Corydoras catfish, are primarily bottom-feeders and scavenge for food particles in the substrate.
Overall, catfish are adaptable and have a flexible diet, allowing them to thrive in various aquatic environments.
Is a Catfish a Producer, Consumer or Decomposer?
A catfish is a consumer. In ecological terms, consumers are organisms that obtain their energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms.
Catfish are predatory fish that feed on other aquatic organisms such as smaller fish, insects, and invertebrates.
They are considered secondary consumers because they typically feed on smaller animals that are themselves consumers or primary consumers, which are organisms that directly feed on producers (plants or algae).
What Type of Consumer is a Catfish?
Catfish are typically classified as secondary consumers or, more specifically, as mesopredators in aquatic ecosystems. As secondary consumers, they occupy an intermediate position in the food chain, feeding on primary consumers (such as insects and small invertebrates) and being preyed upon by larger predators.
There are numerous species of catfish, each with its own ecological niche and dietary preferences. Here are a few examples:
- Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus): This species is commonly found in North America and is known to have a varied diet. Channel catfish are opportunistic feeders, consuming both plant and animal matter. They eat insects, crustaceans, mollusks, small fish, and plant material.
- Walking Catfish (Clarias spp.): Walking catfish are a group of air-breathing catfish species found in Southeast Asia and Africa. They have adapted to living in oxygen-deprived or stagnant waters. Walking catfish are primarily omnivorous and feed on insects, small fish, crustaceans, and plant matter.
- Electric Catfish (Malapterurus electricus): These catfish species inhabit freshwater rivers and lakes in Africa. They have specialized electric organs that they use for navigation, communication, and hunting. Electric catfish are primarily piscivorous, feeding on other fish, but they also consume insects, crustaceans, and mollusks.
- Glass Catfish (Kryptopterus spp.): Glass catfish are known for their transparent bodies, and they are native to Southeast Asia. They are omnivorous, feeding on small insects, worms, crustaceans, and plant matter. They are also popular aquarium fish.
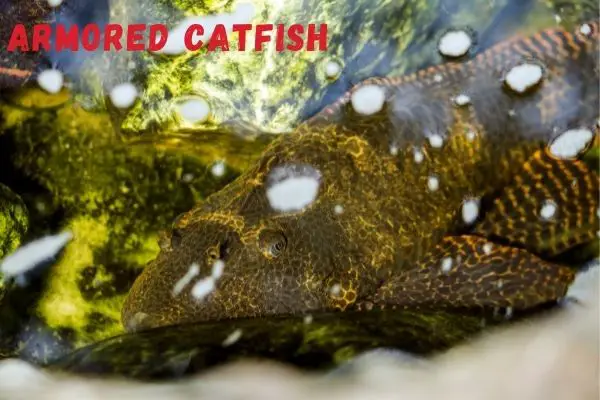
- Armored Catfish: This catfish species, commonly referred to as plecos or plecostomus, is native to South America. They have a specialized mouth structure that allows them to scrape algae and biofilm off surfaces. Armored catfish are primarily herbivorous, but they will also consume other food sources like invertebrates and detritus.
These are just a few examples of the diverse dietary habits within the catfish family. The specific feeding behavior of a catfish species is influenced by factors such as its anatomy, habitat, availability of food sources, and ecological niche.
Can Catfish be Considered Decomposers?
No, catfish are not considered decomposers but are among the few fish species that are scavengers.
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler substances. They play a crucial role in the process of decomposition and nutrient recycling in ecosystems. Examples of decomposers include bacteria, fungi, and some invertebrates like earthworms.

A crucial difference between scavengers and decomposers is that scavengers simply break animals down into smaller pieces; they do not break them down into basic chemical nutrients as decomposers do.
In fact, no fish can be considered a true decomposer.
Where are Catfish in the Food Chain?
Catfish are positioned at various levels in the food chain depending on the specific habitat and ecosystem they inhabit. Generally, catfish can be found at different trophic levels, including both higher and lower positions in the food chain.
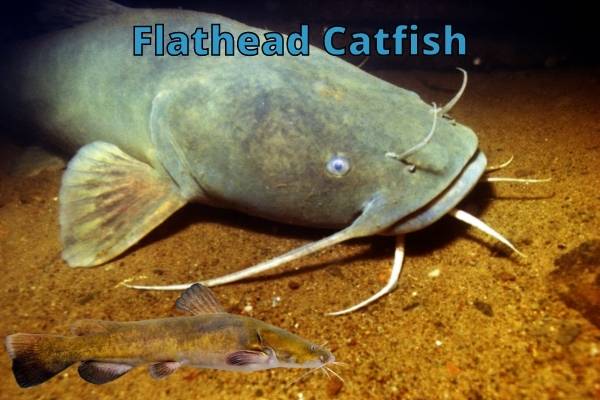
As predators, catfish sit at the top of the food chain and are considered tertiary consumers. But it depends on the species of catfish as some are very small and some (like the flathead catfish) are large and almost without natural predators.
Catfish are primarily carnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources such as insects, smaller fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and even plant matter. Some catfish species are opportunistic scavengers, consuming dead organic material and debris. As such, they often play a vital role in the ecosystem by helping to clean up and recycle nutrients.
In certain environments, catfish can be considered secondary or tertiary consumers. They may consume smaller fish or invertebrates that occupy lower trophic levels, making them higher-level predators in the food chain. In this scenario, they obtain energy by consuming other organisms that have already converted energy from primary producers (such as plants or algae).
However, it’s important to note that the position of catfish in the food chain can vary depending on the specific species, their size, the ecosystem they inhabit, and the availability of food sources. Different catfish species have diverse feeding habits and occupy different niches within their respective ecosystems.

The vast majority of a catfish’s diet is composed of small invertebrates like insects, worms, and they love crustaceans like crayfish and molluscs, but they may also eat other smaller catfish, frogs, and birds that themselves consume animals.
Are Catfish Autotrophs or Heterotrophs?
Catfish are heterotrophs because they eat other living organisms. Practically no animals are autotrophic because most animals do not get their energy from inorganic materials like some bacteria and all plants do.
That is, animals like the catfish do not make their own energy, but need to eat other organisms as their energy and carbon source. However, some animals have such a close relationship with algae that they are almost autotrophic!
What Animals Hunt and Eat Catfish?
While catfish may be at the top of the food chain, they are not without their own predators.
Some of the most common predators of catfish are other larger catfish and large birds like eagles, hawks, and owls, but also other fish like pike, bass, and carp.
Here are some examples:
- Large predatory fish: Species such as pike, muskellunge, largemouth bass, and striped bass are known to prey on catfish. These fish are powerful swimmers and have sharp teeth that allow them to catch and consume catfish.
- Birds of prey: Various birds, including herons, egrets, ospreys, and eagles, feed on catfish. These birds are skilled hunters and often snatch catfish from the water surface or shallow areas near the shore.
- Otters: These semi-aquatic mammals have a diverse diet and are opportunistic hunters. They are known to catch and consume catfish, along with other fish species.
- Alligators and crocodiles: In regions where catfish and these reptiles coexist, alligators and crocodiles are known to hunt and consume catfish. They are highly capable predators in water and have powerful jaws to capture their prey.
- Snapping turtles: These aquatic turtles are opportunistic feeders and will eat almost anything that comes their way. They are known to consume catfish, particularly smaller individuals.
- Humans: Catfish are widely sought after by fishermen and are popular in many cuisines around the world. People catch catfish for both sport and commercial purposes.
It’s worth noting that the predators targeting catfish may vary depending on the specific geographical location, habitat, and size of the catfish.
Some land-dwellers like foxes and raccoons may also catch and eat catfish occasionally.
Humans also pose a threat to catfish through hunting and habitat destruction.
Conclusion
In this post I have looked into the dietary preferences of the catfish and the role they play in the food chain. Catfish are very good at finding food and they are not picky when it comes to food choices.
Catfish are a very interesting fish because they are omnivores but they have a diet based heavily on scavenging!
Catfish are scavengers and they are important to the food chain because they clean up the environment. They are the top-level predators in their ecosystems and their diet is very important to the food chain.
However, despite being scavengers, they are not true decomposers although there are other animals that are decomposers in the ocean.
Catfish are very important in many ecosystems and they are a very good indicator of environmental health.
They are also very good at adapting to their environment and their diet.
They are also very hard to catch and they are very good at hiding in the mud, so you may have to be patient to catch them!
If you are interested in the role that fish scavengers play in the food chain check my other posts on this blog.