Most bees are primary consumers because they mainly eat plant-based food, such as nectar, pollen and sap. However, some bee species, like the vulture bee, will also eat meat and are therefore secondary consumers.
Bees are flying insects that are closely related to wasps and ants. They are known for their role in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey.
Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamily Apoidea and are presently considered a clade, called Anthophila. There are nearly 20,000 known species of bees in seven to nine recognized families though many of these families contain only a single genus.
Bees can be found in various habitats, including forests, deserts, and mountains. They cannot live in Antarctica or the arctic because it is too cold.
Honey bees are social insects that build large hives where they live as a colony. In contrast, solitary bees make nests in burrows in the ground or in holes in wood, where they stash food and lay their eggs.1
Contents
Are bees primary consumers?
Bees can be primary, secondary and even tertiary consumers, depending on their diet. Primary consumers are organisms that feed on producers.
Secondary consumers are consumers that feed on primary consumers, tertiary consumers feed on secondary consumers, etc.
Most bees, like honey bees, are primary consumers because they only eat plants. However, bees can also be parasitic3 or carnivorous4.
Bees are flying insects that are closely related to wasps and ants. They play an important role in pollinating flowering plants and producing honey. Bees feed on plant-based food, such as nectar, pollen and sap.
These are sources of carbohydrates, proteins and minerals for the bees. Most bees are primary consumers because they mainly eat producers. Primary consumers are organisms that eat autotrophs, such as plants, algae or bacteria.

Autotrophs make their own organic molecules from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water. Some examples of autotrophs are grass, lettuce, seaweed and phytoplankton .
However, not all bees are primary consumers. Some bee species, like the vulture bee, will also eat meat and are therefore secondary consumers. Secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers.
They are usually carnivores or omnivores. Carnivores are animals that eat other animals, while omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals.
For instance, a fox is a secondary consumer that eats rabbits, which are primary consumers that eat grass . The vulture bee is a secondary consumer that eats carrion, which is the decaying flesh of dead animals.
In summary, bees can be either primary or secondary consumers depending on their diet. Most bees are primary consumers that feed on plant-based food, while some bees are secondary consumers that feed on meat as well.
Pollen is the male reproductive cells of flowers and are rich in protein and other nutrients2. Bees are attracted to the sweet fragrances and bright colors of flowers.
Examples of Bees that are Primary Consumers?
As mentioned before, most bees are primary consumers that feed on nectar and pollen from plants.
Apart for the well-known honey bee, there are many species of solitary bees including carpenter bees, mason bees, mining bees and the hairy-footed flower bee3 that are all examples of primary consumers.
Examples of Bees that are Secondary Consumers?
A small number of bees are secondary consumers that feed on insects or other animals.
Nomad, and sharp-tailed bee larvae are secondary consumers since they feed on the eggs and larvae of other bees.
The female lays her eggs inside the nests of other bees. When they hatch, the larvae eat the host’s eggs, larvae, and food stores.3
The adults of these bees are, however, vegetarian like other bees.
The vulture bee, found in North and South America is the only bee carnivore. While they will eat nectar and pollen, they prefer carrion.
Vulture bees are social insects, like honey bees, and produce a honey-like substance from the carrion they carry back to the hive.4
What are Examples of Bees that are Tertiary Consumers?
Vulture bees may be considered tertiary or quaternary consumers if they feed on the carrion of omnivorous or carnivorous animals.
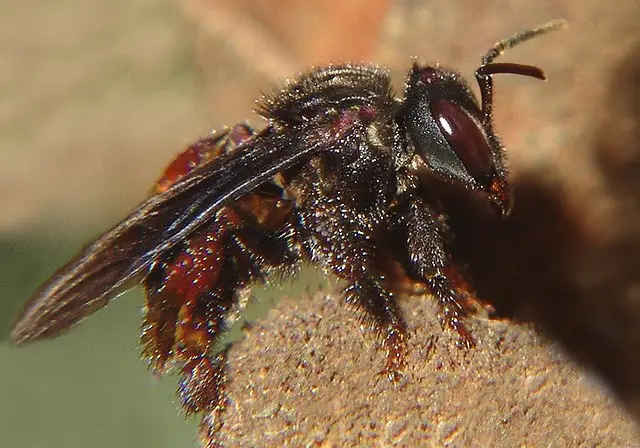

Although they mostly eat dead animals, they may also attack inactive or diseased animals. Vulture bees will mostly be secondary consumers, but may also eat dead or alive secondary consumers, which makes them tertiary or even quaternary consumers.
Where are Bees in the Food Chain?
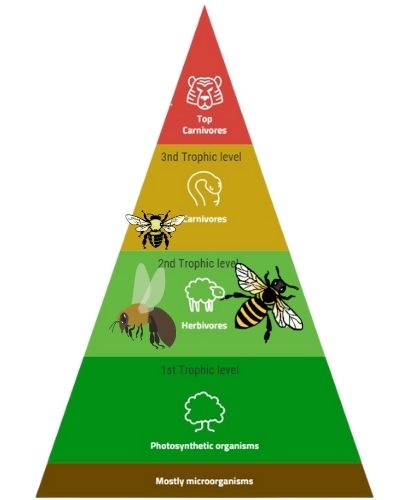
Bees are on the second trophic level in the energy pyramid, just above the plants that they feed on. They are also eaten by many other organisms, making them an important part of the food chain.
Bees are important in the food chain because they help pollinate plants. Pollination is necessary for plant reproduction, and wild bees are one of the most important pollinators in the world.
Bees collect nectar from flowers and spread pollen as they move from flower to flower. This process helps fertilize plants and allows them to produce fruits, vegetables, and nuts that in turn spreads the plants around so that other, primary consumers, have something to eat!
The decline in bee populations has been a cause for concern in recent years, as it could have a negative impact on food chains around the world.
Are any Bees Decomposers?
No, bees are not decomposers. Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler substances.
They play a crucial role in the process of decomposition, which helps recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. Examples of decomposers include bacteria, fungi, and certain types of insects like beetles and maggots.
Bees, on the other hand, are not decomposers. They are pollinators, meaning they help transfer pollen from the male parts of flowers to the female parts, enabling plants to reproduce.
Bees collect nectar and pollen from flowers, which they use as food for themselves and their offspring. While bees do play a vital role in the ecosystem by pollinating plants, they do not participate in the decomposition process.
However, the vulture bee may be considered a scavenger, since they feed on the meat of dead animals.
True decomposers, however, not only feed on dead organic matter but also break them down into chemical nutrients.
Can Bees be Producers?
Bees are heterotrophs because they eat other living organisms. Practically no animals are autotrophic because animals do not get their energy directly from the sun like plants do. That is, animals like bees cannot make their own energy!
While bees themselves do not undergo photosynthesis, they indirectly contribute to the production of energy-rich organic compounds through their role as pollinators. Bees visit flowers to collect nectar and pollen.
Nectar is a sugary substance produced by flowers and serves as the primary energy source for bees.
During their foraging, bees inadvertently transfer pollen from the male reproductive parts of one flower to the female reproductive parts of another, facilitating pollination and enabling the production of fruits, seeds, and other plant reproductive structures.
By aiding in the pollination process, bees contribute to the reproduction and growth of plants, which are the primary producers in most terrestrial ecosystems. Through this interaction, bees play a crucial role in maintaining the productivity and diversity of plant communities, which supports the overall functioning of ecosystems.
Why are Bees not Producers?
Bees are not producers because they cannot produce their own chemical energy. Bees need to eat other organisms to gain energy.
Producers, like plants and algae, and some bacteria, generate their own chemical energy from sunlight, through photosynthesis or through chemosynthesis using other inorganic compounds.
What Animals Prey on Bees?
Bees are food for a variety of animals including birds, mammals, wasps, flies, spiders and even other bees. Flower crab spiders are masters of camouflage that sit and wait inside flowers for bees to visit5.

As soon as an unsuspecting bee gets close enough, the spider grabs them and eats them.
Additionally, many animals feed on the honey or wax produced by honey bees. Humans and honey badgers are examples of animals that enjoy honey.
Honey guides, on the other hand, are birds that prefer the wax found inside the beehive.6
However, today sadly more and more bees die not due to predation but due to pesticides and habitat destruction.
Conclusion
In this blog post, I have looked into the diet of the bee as an animal that is rarely thought about on a day to day basis.
Bees are important pollinators of both crops and wild plants. They transfer pollen from the male organ or stamen of a flower to the female organ or pistil. Fertilization can then take place, resulting in the production of seeds.
About one third of the food that we eat depends on pollination by animals, with bees being responsible for up to 80% of this pollination in some areas.
The estimated value of global crop production that is attributable to bee pollination is $153 billion per year! That’s a lot of honey!
Bees are under threat from habitat loss, pesticide use and climate change. We need to do our part to protect these important creatures!
The importance of bees cannot be underestimated, and I hope you enjoy reading this blog post!
References
- Tutus loco. 2022. About solitary bees. https://www.beehotels.co.za/pages/solitary-bees
- United Stated Geological Survey. Do bees feed on both nectar and pollen? https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/do-bees-feed-both-nectar-and-pollen
- Wildcare Nationwide Ecology Supplies. Solitary Bees: 8 facts to know plus an identification resource. https://www.wildcare.co.uk/blog/solitary-bees-8-facts-to-know-plus-an-identification-resource/
- Gamillo E. 2021. Why Vulture Bees Prefer Rotting Flesh Over Pollen. The Smithsonian Magazine. https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/vulture-bees-have-specialized-microbiomes-that-aid-their-taste-in-meat-180979131/
- Larsen N. Thomisus (flower crab spiders). Iziko Museums of South Africa. http://www.biodiversityexplorer.info/arachnids/spiders/thomisidae/thomisus.htm
- African Honeyguides. https://africanhoneyguides.com/




